imputomics: web server and R package for missing values imputation in metabolomics data
- PMID: 38377398
- PMCID: PMC10918629
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btae098
imputomics: web server and R package for missing values imputation in metabolomics data
Abstract
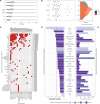
Motivation: Missing values are commonly observed in metabolomics data from mass spectrometry. Imputing them is crucial because it assures data completeness, increases the statistical power of analyses, prevents inaccurate results, and improves the quality of exploratory analysis, statistical modeling, and machine learning. Numerous Missing Value Imputation Algorithms (MVIAs) employ heuristics or statistical models to replace missing information with estimates. In the context of metabolomics data, we identified 52 MVIAs implemented across 70 R functions. Nevertheless, the usage of those 52 established methods poses challenges due to package dependency issues, lack of documentation, and their instability.
Results: Our R package, 'imputomics', provides a convenient wrapper around 41 (plus random imputation as a baseline model) out of 52 MVIAs in the form of a command-line tool and a web application. In addition, we propose a novel functionality for selecting MVIAs recommended for metabolomics data with the best performance or execution time.
Availability and implementation: 'imputomics' is freely available as an R package (github.com/BioGenies/imputomics) and a Shiny web application (biogenies.info/imputomics-ws). The documentation is available at biogenies.info/imputomics.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Armitage EG, Godzien J, Alonso-Herranz V. et al. Missing value imputation strategies for metabolomics data. Electrophoresis 2015;36:3050–60. - PubMed
-
- Chang W, Cheng J, Allaire J. et al. Shiny: Web Application Framework for R, 2024. https://github.com/rstudio/shiny.
-
- Josse J, Husson F.. missMDA: a package for handling missing values in multivariate data analysis. J Stat Soft 2016;70:1–31.

