Alcohol induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation in the brain of rats is attenuated by ATRA supplementation
- PMID: 38377424
- PMCID: PMC8474578
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbih.2019.100024
Alcohol induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation in the brain of rats is attenuated by ATRA supplementation
Abstract
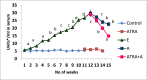
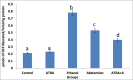
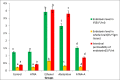
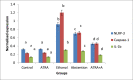
Alcohol abuse affects several neurological pathways and causes significant alterations in the brain. Abstention from alcohol is an effective intervention against alcohol related diseases. But the recovery of the damaged cells to normal presents a major problem in those who have stopped alcohol consumption. Hence therapeutic interventions are needed. Our previous studies have shown that all trans retinoic acid (ATRA) is effective in reducing alcohol induced neuro toxicity. Chronic alcohol administration up-regulates and activates the NLRP3 inflammasome leading to caspase-1 activation and IL-1β production causing neuroinflammation. Hence, we investigated whether ATRA has any impact on NLRP3 inflammasomes activation. Rats were divided into two groups and were maintained for 90 days as control and ethanol group (4 g/kg body weight). After 90 days, ethanol administration was stopped and animals in the control group were divided into control and control + ATRA (100 μg/kg body weight per day) groups; those in the ethanol group as ethanol abstention and ATRA (100 μg/kg body weight per day) and maintained for 30 days. Administration of ATRA reduced reactive oxygen species and endotoxins which were elevated in alcoholic rats. There was also reduction in the expression of NLRP3 inflammasome and caspase 1. Our results suggested ATRA down regulated NLRP3 activation with concomitant decrease in the release of caspase -1 and production of IL1β. However, all these parameters were higher in abstention in comparison with ATRA supplemented group. In short therapeutic intervention with ATRA regressed alcohol induced inflammasome activation better than abstention.
Keywords: ATRA; Caspase-1; Endotoxins; IL-1β; NLRP3.
© 2019 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that we have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
All Trans Retinoic Acid Attenuates Markers of Neuroinflammation in Rat Brain by Modulation of SIRT1 and NFκB.Neurochem Res. 2018 Sep;43(9):1791-1801. doi: 10.1007/s11064-018-2595-7. Epub 2018 Jul 18. Neurochem Res. 2018. PMID: 30022380
-
Alcohol-induced IL-1β in the brain is mediated by NLRP3/ASC inflammasome activation that amplifies neuroinflammation.J Leukoc Biol. 2013 Jul;94(1):171-82. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1212659. Epub 2013 Apr 26. J Leukoc Biol. 2013. PMID: 23625200 Free PMC article.
-
All-Trans Retinoic Acid Enhances both the Signaling for Priming and the Glycolysis for Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome in Human Macrophage.Cells. 2020 Jul 1;9(7):1591. doi: 10.3390/cells9071591. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32630207 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen-Rich Saline Attenuated Subarachnoid Hemorrhage-Induced Early Brain Injury in Rats by Suppressing Inflammatory Response: Possible Involvement of NF-κB Pathway and NLRP3 Inflammasome.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Jul;53(5):3462-3476. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9242-y. Epub 2015 Jun 20. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26091790
-
Mechanisms of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation: Its Role in the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease.Neurochem Res. 2020 Nov;45(11):2560-2572. doi: 10.1007/s11064-020-03121-z. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Neurochem Res. 2020. PMID: 32929691 Review.
Cited by
-
Nuclear Receptors as Multiple Regulators of NLRP3 Inflammasome Function.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 26;12:630569. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.630569. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33717162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acetylsalicylic Acid Suppresses Alcoholism-Induced Cognitive Impairment Associated with Atorvastatin Intake by Targeting Cerebral miRNA155 and NLRP3: In Vivo, and In Silico Study.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Feb 27;14(3):529. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14030529. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35335908 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol Increases Lung Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Expression and Exacerbates Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Spike Protein Subunit 1-Induced Acute Lung Injury in K18-hACE2 Transgenic Mice.Am J Pathol. 2022 Jul;192(7):990-1000. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2022.03.012. Epub 2022 Apr 25. Am J Pathol. 2022. PMID: 35483427 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Ethanol Modulates Synaptic Inhibition in the Basolateral Amygdala via Rapid NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Regulates Anxiety-Like Behavior in Rats.J Neurosci. 2023 Nov 22;43(47):7902-7912. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1744-22.2023. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37739795 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoic acid differently modulates NOD1/NOD2-mediated inflammatory responses in human macrophage subsets.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 1;16:1609763. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1609763. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40666513 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abhilash P.A., Harikrishnan R., Indira M. Ascorbic acid supplementation down-regulates the alcohol induced oxidative stress, hepatic stellate cell activation, cytotoxicity and mRNA levels of selected fibrotic genes in Guinea pigs. Free Radic. Res. 2012;46(2):204–213. - PubMed
-
- Abo-Ouf H., Hooper A.W., White E.J., van Rensburg H.J., Trigatti B.L., Igdoura S.A. Deletion of tumor necrosis factor-α ameliorates neurodegeneration in Sandhoff disease mice. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013;22:3960–3975. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

