Comprehensive Impurity Profiling of mRNA: Evaluating Current Technologies and Advanced Analytical Techniques
- PMID: 38377434
- PMCID: PMC10918618
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.3c05539
Comprehensive Impurity Profiling of mRNA: Evaluating Current Technologies and Advanced Analytical Techniques
Abstract
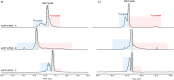
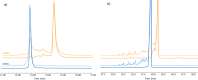
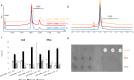
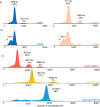
In vitro transcription (IVT) of mRNA is a versatile platform for a broad range of biotechnological applications. Its rapid, scalable, and cost-effective production makes it a compelling choice for the development of mRNA-based cancer therapies and vaccines against infectious diseases. The impurities generated during mRNA production can potentially impact the safety and efficacy of mRNA therapeutics, but their structural complexity has not been investigated in detail yet. This study pioneers a comprehensive profiling of IVT mRNA impurities, integrating current technologies with innovative analytical tools. We have developed highly reproducible, efficient, and stability-indicating ion-pair reversed-phase liquid chromatography and capillary gel electrophoresis methods to determine the purity of mRNA from different suppliers. Furthermore, we introduced the applicability of microcapillary electrophoresis for high-throughput (<1.5 min analysis time per sample) mRNA impurity profiling. Our findings revealed that impurities are mainly attributed to mRNA variants with different poly(A) tail lengths due to aborted additions or partial hydrolysis and the presence of double-stranded mRNA (dsRNA) byproducts, particularly the dsRNA 3'-loop back form. We also implemented mass photometry and native mass spectrometry for the characterization of mRNA and its related product impurities. Mass photometry enabled the determination of the number of nucleotides of different mRNAs with high accuracy as well as the detection of their size variants [i.e., aggregates and partial and/or total absence of the poly(A) tail], thus providing valuable information on mRNA identity and integrity. In addition, native mass spectrometry provided insights into mRNA intact mass, heterogeneity, and important sequence features such as poly(A) tail length and distribution. This study highlights the existing bottlenecks and opportunities for improvement in the analytical characterization of IVT mRNA, thus contributing to the refinement and streamlining of mRNA production, paving the way for continued advancements in biotechnological applications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


References
-
- Rhoads R. E.Synthetic mRNA: Production, Introduction into Cells, and Physiological Consequences. In Synthetic mRNA; Rhoads R. E., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer New York: New York, NY, 2016; Vol. 1428, pp 3–27. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

