Intranasal B5 promotes mucosal defence against Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae via ameliorating early immunosuppression
- PMID: 38378464
- PMCID: PMC10880497
- DOI: 10.1080/21505594.2024.2316459
Intranasal B5 promotes mucosal defence against Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae via ameliorating early immunosuppression
Abstract
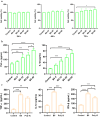
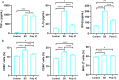
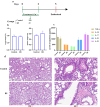
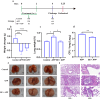
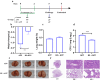
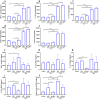
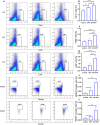
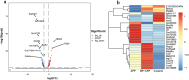
Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae (APP) is an important pathogen of the porcine respiratory disease complex, which leads to huge economic losses worldwide. We previously demonstrated that Pichia pastoris-producing bovine neutrophil β-defensin-5 (B5) could resist the infection by the bovine intracellular pathogen Mycobacterium bovis. In this study, the roles of synthetic B5 in regulating mucosal innate immune response and protecting against extracellular APP infection were further investigated using a mouse model. Results showed that B5 promoted the production of tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, and interferon (IFN)-β in macrophages as well as dendritic cells (DC) and enhanced DC maturation in vitro. Importantly, intranasal B5 was safe and conferred effective protection against APP via reducing the bacterial load in lungs and alleviating pulmonary inflammatory damage. Furthermore, in the early stage of APP infection, we found that intranasal B5 up-regulated the secretion of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-17, and IL-22; enhanced the rapid recruitment of macrophages, neutrophils, and DC; and facilitated the generation of group 3 innate lymphoid cells in lungs. In addition, B5 activated signalling pathways associated with cellular response to IFN-β and activation of innate immune response in APP-challenged lungs. Collectively, B5 via the intranasal route can effectively ameliorate the immune suppression caused by early APP infection and provide protection against APP. The immunization strategy may be applied to animals or human respiratory bacterial infectious diseases. Our findings highlight the potential importance of B5, enhancing mucosal defence against intracellular bacteria like APP which causes early-phase immune suppression.
Keywords: Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae; Group 3 innate lymphoid cells; bovine neutrophil β-defensin-5; immune suppression; mucosal defence.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bovine Neutrophil β-Defensin-5 Provides Protection against Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae via Regulating Pulmonary Inflammatory Response and Metabolic Response.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 29;25(19):10506. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910506. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408834 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal bovine β-defensin-5 enhances antituberculosis immunity in a mouse model by a novel protein-based respiratory mucosal vaccine.Virulence. 2022 Dec;13(1):949-962. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2022.2080342. Virulence. 2022. PMID: 35603910 Free PMC article.
-
Nasal immunization with major epitope-containing ApxIIA toxin fragment induces protective immunity against challenge infection with Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae in a murine model.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2013 Jan 15;151(1-2):102-12. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2012.10.011. Epub 2012 Nov 9. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2013. PMID: 23200821
-
High-dimensional analysis reveals an immune atlas and novel neutrophil clusters in the lungs of model animals with Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae-induced pneumonia.Vet Res. 2023 Sep 13;54(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s13567-023-01207-4. Vet Res. 2023. PMID: 37705063 Free PMC article.
-
Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae: The molecular determinants of virulence and pathogenesis.Adv Microb Physiol. 2021;78:179-216. doi: 10.1016/bs.ampbs.2020.12.001. Epub 2021 Jan 25. Adv Microb Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34147185 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunization of pigs with Actinobacillus pleuropneumonia live attenuated (gene-deleted) vaccine HB04M intramuscularly or intranasally exhibits remarkably rapid protection against heterologous strain challenge.BMC Vet Res. 2025 Jul 8;21(1):450. doi: 10.1186/s12917-025-04895-6. BMC Vet Res. 2025. PMID: 40629392 Free PMC article.
-
Bovine Neutrophil β-Defensin-5 Provides Protection against Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae via Regulating Pulmonary Inflammatory Response and Metabolic Response.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 29;25(19):10506. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910506. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408834 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gottschalk M, Broes A.. Actinobacillosis. In Zimmerman JJ, Karriker LA, Ramirez A, et al., editors. Diseases of swine. Chichester: Wiley; 2019. p. 749–17.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
