The prostate-specific membrane antigen holds potential as a vascular target for endogenous radiotherapy with [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-I&T for triple-negative breast cancer
- PMID: 38378689
- PMCID: PMC10877802
- DOI: 10.1186/s13058-024-01787-9
The prostate-specific membrane antigen holds potential as a vascular target for endogenous radiotherapy with [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-I&T for triple-negative breast cancer
Abstract
Introduction: Overexpression of prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) on the vasculature of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) presents a promising avenue for targeted endogenous radiotherapy with [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-I&T. This study aimed to assess and compare the therapeutic efficacy of a single dose with a fractionated dose of [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-I&T in an orthotopic model of TNBC.
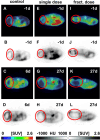
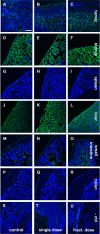
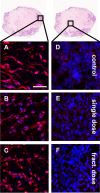
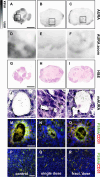
Methods: Rj:NMRI-Foxn1nu/nu mice were used as recipients of MDA-MB-231 xenografts. The single dose group was treated with 1 × 60 ± 5 MBq dose of [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-I&T, while the fractionated dose group received 4 × a 15 ± 2 MBq dose of [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-I&T at 7 day intervals. The control group received 0.9% NaCl. Tumor progression was monitored using [18F]FDG-PET/CT. Ex vivo analysis encompassed immunostaining, TUNEL staining, H&E staining, microautoradiography, and autoradiography.
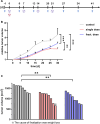
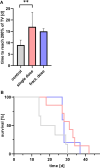
Results: Tumor volumes were significantly smaller in the single dose (p < 0.001) and fractionated dose (p < 0.001) groups. Tumor growth inhibition rates were 38% (single dose) and 30% (fractionated dose). Median survival was notably prolonged in the treated groups compared to the control groups (31d, 28d and 19d for single dose, fractionated dose and control, respectively). [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-I&T decreased the size of viable tumor areas. We further demonstrated, that [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-I&T binds specifically to the tumor-associated vasculature.
Conclusion: This study highlights the potential of [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-I&T for endogenous radiotherapy of TNBC.
Keywords: Anti-angiogenic therapy; Endogenous radiotherapy; Orthotopic xenograft; Prostate-specific membrane antigen; Triple-negative breast cancer.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
FMM is medical advisor for Nanomab Technology Ltd. and Advanced Accelerator Applications (AAA) GmbH. He has recently received institutional grants from Nanomab Technology Ltd., Siemens and GE Precision Healthcare LLC. Furthermore he has an interventional research contract with CURIUM.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

