Selpercatinib combination with the mitochondria-targeted antioxidant MitoQ effectively suppresses RET-mutant thyroid cancer
- PMID: 38378752
- PMCID: PMC10879150
- DOI: 10.1038/s41698-024-00536-7
Selpercatinib combination with the mitochondria-targeted antioxidant MitoQ effectively suppresses RET-mutant thyroid cancer
Abstract
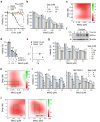
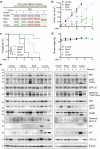
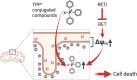
Genetic alternation of REarranged during Transfection (RET) that leads to constitutive RET activation is a crucial etiological factor for thyroid cancer. RET is known to regulate mitochondrial processes, although the underlying molecular mechanisms remain unclear. We previously showed that the multi-kinase inhibitors vandetanib and cabozantinib increase the mitochondrial membrane potential (Δψm) in RET-mutated thyroid tumor cells and that this effect can be exploited to increase mitochondrial enrichment of Δψm-sensitive agents in the tumor cells. In this study, we hypothesized that the RET-selective inhibitor, selpercatinib, can increase Δψm and, subsequently, tumor cell uptake of the mitochondria-targeted ubiquinone (MitoQ) to the level to break the mitochondrial homeostasis and induce lethal responses in RET-mutated thyroid tumor cells. We show that selpercatinib significantly increased Δψm, and its combination with MitoQ synergistically suppressed RET-mutated human thyroid tumor cells, which we validated using RET-targeted genetic approaches. Selpercatinib and MitoQ, in combination, also suppressed CCDC6-RET fusion cell line xenografts in mice and prolonged animal survival more effectively than single treatments of each agent. Moreover, we treated two patients with CCDC6-RET or RETM918T thyroid cancer, who could not take selpercatinib at regular doses due to adverse effects, with a dose-reduced selpercatinib and MitoQ combination. In response to this combination therapy, both patients showed tumor reduction. The quality of life of one patient significantly improved over a year until the tumor relapsed. This combination of selpercatinib with MitoQ may have therapeutic potential for patients with RET-mutated tumors and intolerant to regular selpercatinib doses.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Erlotinib combination with a mitochondria-targeted ubiquinone effectively suppresses pancreatic cancer cell survival.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Feb 21;30(7):714-727. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i7.714. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38515951 Free PMC article.
-
Selpercatinib for adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic RET-altered solid tumors.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2023 Jul-Dec;23(11):1117-1122. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2023.2267754. Epub 2023 Oct 27. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2023. PMID: 37795873 Review.
-
Efficacy of Selpercatinib in RET-Altered Thyroid Cancers.N Engl J Med. 2020 Aug 27;383(9):825-835. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2005651. N Engl J Med. 2020. PMID: 32846061 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
D898_E901 RET Deletion Is Oncogenic, Responds to Selpercatinib, and Treatment Resistance Can Arise Via RET-Independent Mechanisms.JCO Precis Oncol. 2023 Aug;7:e2300052. doi: 10.1200/PO.23.00052. JCO Precis Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37535881 Free PMC article.
-
Selpercatinib: A Review in Advanced RET Fusion-Positive NSCLC.Target Oncol. 2023 Jan;18(1):169-176. doi: 10.1007/s11523-022-00935-5. Epub 2022 Nov 24. Target Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36422787 Review.
Cited by
-
Altered Mitochondrial Function in MASLD: Key Features and Promising Therapeutic Approaches.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jul 26;13(8):906. doi: 10.3390/antiox13080906. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199152 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

