Enhancing (2S)-naringenin production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by high-throughput screening method based on ARTP mutagenesis
- PMID: 38379664
- PMCID: PMC10874921
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-023-03892-6
Enhancing (2S)-naringenin production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by high-throughput screening method based on ARTP mutagenesis
Abstract
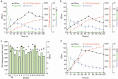
(2S)-Naringenin, a dihydro-flavonoid, serves as a crucial precursor for flavonoid synthesis due to its extensive medicinal values and physiological functions. A pathway for the synthesis of (2S)-naringenin from glucose has previously been constructed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae through metabolic engineering. However, this synthetic pathway of (2S)-naringenin is lengthy, and the genes involved in the competitive pathway remain unknown, posing challenges in significantly enhancing (2S)-naringenin production through metabolic modification. To address this issue, a novel high-throughput screening (HTS) method based on color reaction combined with a random mutagenesis method called atmospheric room temperature plasma (ARTP), was established in this study. Through this approach, a mutant (B7-D9) with a higher titer of (2S)-naringenin was obtained from 9600 mutants. Notably, the titer was enhanced by 52.3% and 19.8% in shake flask and 5 L bioreactor respectively. This study demonstrates the successful establishment of an efficient HTS method that can be applied to screen for high-titer producers of (2S)-naringenin, thereby greatly improving screening efficiency and providing new insights and solutions for similar product screenings.
Keywords: (2S)-Naringenin; Atmospheric room temperature plasma; Color reaction; High-throughput screening; Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
© King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Cao S, Zhou X, Jin W, Wang F, Tu R, Han S, Chen H, Chen C, Xie G-J, Ma F. Improving of lipid productivity of the oleaginous microalgae Chlorella pyrenoidosa via atmospheric and room temperature plasma (ARTP) Bioresour Technol. 2017;244(2):1400–1406. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.05.039. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

