Piezoelectric hydrogel for treatment of periodontitis through bioenergetic activation
- PMID: 38379699
- PMCID: PMC10876489
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.02.011
Piezoelectric hydrogel for treatment of periodontitis through bioenergetic activation
Abstract
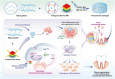
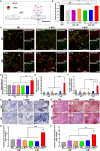
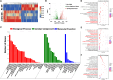
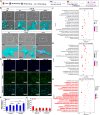
The impaired differentiation ability of resident cells and disordered immune microenvironment in periodontitis pose a huge challenge for bone regeneration. Herein, we construct a piezoelectric hydrogel to rescue the impaired osteogenic capability and rebuild the regenerative immune microenvironment through bioenergetic activation. Under local mechanical stress, the piezoelectric hydrogel generated piezopotential that initiates osteogenic differentiation of inflammatory periodontal ligament stem cells (PDLSCs) via modulating energy metabolism and promoting adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthesis. Moreover, it also reshapes an anti-inflammatory and pro-regenerative niche through switching M1 macrophages to the M2 phenotype. The synergy of tilapia gelatin and piezoelectric stimulation enhances in situ regeneration in periodontal inflammatory defects of rats. These findings pave a new pathway for treating periodontitis and other immune-related bone defects through piezoelectric stimulation-enabled energy metabolism modulation and immunomodulation.
Keywords: Bone regeneration; Macrophage polarization; Mitochondrial bioenergetics; Periodontitis; Piezoelectric hydrogel.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures






References
-
- Kinane D.F., Stathopoulou P.G., Papapanou P.N. Periodontal diseases. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017;3(1):1–14. - PubMed
-
- Roth G.A., Abate D., Abate K.H., Abay S.M., Abbafati C., Abbasi N., Abbastabar H., Abd-Allah F., Abdela J., Abdelalim A. Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392(10159):1736–1788. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

