Exploring gene signatures and regulatory networks in a rat model of sciatica: implications and validation in neuropathic pain
- PMID: 38379852
- PMCID: PMC10877633
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1261217
Exploring gene signatures and regulatory networks in a rat model of sciatica: implications and validation in neuropathic pain
Abstract
Background: Sciatica (neuropathic pain [NP]) is a common disease characterized by pain from radiation along the sciatic nerve. The aim of this study was to study the genes associated with chronic systolic injury of sciatic nerve (SCN-CCI) in rats by RNA-Seq technique, and to explore their potential as therapeutic targets.
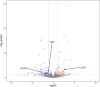
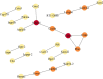
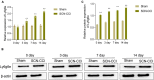
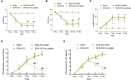
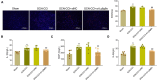
Methods: Sciatic nerve rat model was obtained by ligation of sciatic nerve and divided into two groups: SCN-CCI group and Sham group. Behavioral assessments were performed to evaluate pain sensitivity, following which their spinal cord dorsal horn were resected and RNA sequencing was conducted to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs). Bioinformatics and functional enrichment analysis was performed to identify promising DEGs and their related biological processes and pathways associated with SCN-CCI. PPI network analysis and hub gene identification were conducted. QRT-PCR, western blot, ELISA, and immunofluorescence staining were performed on rat models to validate the expression of these hub genes and investigate related proteins and inflammatory markers.
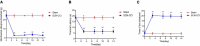
Results: The SCN-CCI rat model was successfully obtained, exhibiting increased pain sensitivity compared to the Sham group, as indicated by decreased mechanical allodynia thresholds, thermal latencies, and increased paw withdrawals. RNA-Seq analysis identified 117 DEGs in the SCN-CCI rat model, involved in various biological processes and pathways related to sciatica. PPI network analysis revealed hub genes, including Ly6g6e, which exhibited significant differential expression. QRT-PCR and Western blot analysis confirmed the expression patterns of these hub genes. Pain behavior assessment demonstrated reduced pain thresholds and increased paw flinching responses in the SCN-CCI group. Furthermore, the SCN-CCI group showed upregulated expression of Ly6g6e, increased protein levels of Ly6g6e, CGRP, and NGF, as well as elevated levels of IL-1β, MCP-1, and IL-6, and microglial cell activation in the spinal dorsal horn. ELISA results confirmed the increased levels of IL-1β, MCP-1, and IL-6 in the spinal dorsal horn.
Conclusion: These comprehensive findings provide valuable insights into the SCN-CCI rat model, DEGs associated with sciatica, hub genes (Ly6g6e as promising targets), pain behavior changes and molecular alterations.
Keywords: RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq); chronic systolic injury of sciatic nerve; differentially expressed genes (DEGs); neuropathic pain (NP); sciatica.
Copyright © 2024 Xu, Wang, Xu, Zhu, Zhang and Yan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
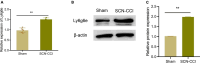

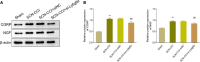
References
-
- Abbaszadeh A., Darabi S., Hasanvand A., Amini-Khoei H., Abbasnezhad A., Choghakhori R., et al. (2018). Minocycline through attenuation of oxidative stress and inflammatory response reduces the neuropathic pain in a rat model of chronic constriction injury. Iran J. Basic Med. Sci. 21 138–144. 10.22038/IJBMS.2017.24248.6053 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Banik R. K., Sia T., Ibrahim M. M., Sivanesan E., Uhelski M., Pena A., et al. (2023). Increases in local skin temperature correlate with spontaneous foot lifting and heat hyperalgesia in both incisional inflammatory models of pain. Pain Rep. 8:e1097. 10.1097/PR9.0000000000001097 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

