Influence of inherent minerals on metalworking fluids sludge pyrolysis: Products characterization and heavy metals behavior
- PMID: 38380051
- PMCID: PMC10877409
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26256
Influence of inherent minerals on metalworking fluids sludge pyrolysis: Products characterization and heavy metals behavior
Abstract
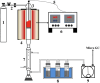
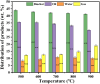
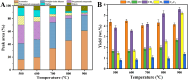
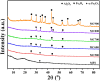
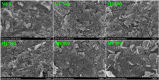
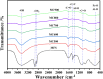
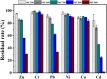
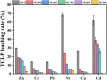
Safely and appropriately disposing of metalworking fluids sludge (MFS) remains a challenge owing to its highly hazardous properties, this work investigated MFS pyrolysis at various temperatures (500, 600, 700, 800, and 900 °C) for energy recovery and safety treatment of MFS. The experimental results indicated that inherent minerals at higher temperatures could enhance the gas yields and promote the qualities of oil and gas from MFS pyrolysis. The highest pyrolysis gas yield was achieved at 18.86 wt% after MFS pyrolysis at 900 °C. GC-MS analysis revealed that the inherent minerals facilitated a decrease in oxygenated and nitrogenated compounds within the oil, while simultaneously leading to a substantial increase in hydrocarbon contents. Notably, the highest content of aromatics (61.16%) was attained during pyrolysis at 900 °C. Moreover, inherent minerals improved carbon sequestration and the characteristics of biochar during the MFS pyrolysis. The leaching contents of heavy metals in biochars were reduced, thereby reducing the heavy metals associated environmental risk. This research suggests that the pyrolysis process was a promising approach for simultaneous energy recovery and MFS disposal with low environmental risk.
Keywords: Characterization; Heavy metals; Metalworking fluids sludge; Product; Pyrolysis.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Guidan Zhu reports financial support was provided by 10.13039/501100015310Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. Hehua Zeng reports financial support was provided by 10.13039/501100001809National Natural Science Foundation of China. Guidan Zhu reports financial support was provided by Natural Science Foundation of Changji University. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Co-pyrolysis of sewage sludge as additive with phytoremediation residue on the fate of heavy metals and the carbon sequestration potential of derived biochar.Chemosphere. 2023 Feb;314:137646. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.137646. Epub 2022 Dec 27. Chemosphere. 2023. PMID: 36581119
-
Influence of pyrolysis temperature on properties and environmental safety of heavy metals in biochars derived from municipal sewage sludge.J Hazard Mater. 2016 Dec 15;320:417-426. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.08.050. Epub 2016 Aug 22. J Hazard Mater. 2016. PMID: 27585274
-
Characteristics of biochars prepared by co-pyrolysis of sewage sludge and cotton stalk intended for use as soil amendments.Environ Technol. 2020 Apr;41(11):1347-1357. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2018.1534891. Epub 2018 Oct 22. Environ Technol. 2020. PMID: 30300096
-
Effect of pyrolysis temperature on characteristics, chemical speciation and risk evaluation of heavy metals in biochar derived from textile dyeing sludge.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2019 Jan 30;168:45-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.10.022. Epub 2018 Oct 25. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2019. PMID: 30384166 Review.
-
A critical review on energy recovery and non-hazardous disposal of oily sludge from petroleum industry by pyrolysis.J Hazard Mater. 2021 Mar 15;406:124706. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124706. Epub 2020 Dec 1. J Hazard Mater. 2021. PMID: 33418275 Review.
References
-
- Lataf A., Jozefczak M., Vandecasteele B., Viaene J., Schreurs S., Carleer R., Yperman J., Marchal W., Cuypers A., Vandamme D. The effect of pyrolysis temperature and feedstock on biochar agronomic properties. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis. 2022;168
-
- Murad Rahimov M.A. Treatment of metal cutting fluid wastewater over Pt/Al2O3 and Ru/Al2O3 in supercritical water medium. J. Water Proc. Eng. 2022;46
-
- Zhang S., Wang F., Mei Z., Lv L., Chi Y. Status and development of sludge incineration in China. Waste and Biomass Valorization. 2021;12:3541–3574.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

