Behind the Mask: Parkinson's Disease and Depression
- PMID: 38380213
- PMCID: PMC10877222
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.52663
Behind the Mask: Parkinson's Disease and Depression
Abstract
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a common, prevalent neurodegenerative disease. It is mainly characterized by motor symptoms such as rigidity, tremors, and bradykinesia, but it can also manifest with non-motor symptoms, of which depression is the most frequent. The latter can impair the quality of life, yet it gets overlooked and goes untreated because of the significant overlap in their clinical features, hence making the diagnosis difficult. Furthermore, there is limited data on the availability of appropriate criteria for making the diagnosis of depression in PD patients, as it can occur with varying expressions throughout the course of PD or it can also precede it. This review article has included a brief discussion on the diagnosis of depression in PD patients and their overlapped clinical manifestations. Understanding the mechanisms underlying the disease processes of PD and depression and the pathways interconnecting them gives better knowledge on devising treatment options for the patients. Only studies from Pubmed were included and all other databases were excluded. Studies from the last 50 years were included. Suitable references included in these studies were also extracted. Thus, depression in PD and PD in depression, along with their pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatment options, have been discussed.
Keywords: anti-depressants; cognitive behavioural therapy; depression; electro-convulsive therapy; neurodegeneration; neuropathology; non-motor symptoms; parkinson' s disease; pimavanserin; treatment of depression in parkinson's disease.
Copyright © 2024, Balasubramanian et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
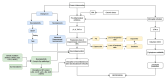
Figures

References
-
- Neurobiology and treatment of Parkinson's disease. Schapira AH. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2009;30:41–47. - PubMed
-
- The epidemiology of Parkinson's disease: risk factors and prevention. Ascherio A, Schwarzschild MA. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15:1257–1272. - PubMed
-
- Epidemiology of Parkinson's disease. Tysnes OB, Storstein A. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 2017;124:901–905. - PubMed
-
- Projected numbers of people with movement disorders in the years 2030 and 2050. Bach JP, Ziegler U, Deuschl G, Dodel R, Doblhammer-Reiter G. Mov Disord. 2011;26:2286–2290. - PubMed
-
- Synaptic failure and α-synuclein. Calo L, Wegrzynowicz M, Santivañez-Perez J, Grazia Spillantini M. Mov Disord. 2016;31:169–177. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
