Effects of Pitavastatin on Coronary Artery Disease and Inflammatory Biomarkers in HIV: Mechanistic Substudy of the REPRIEVE Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 38381407
- PMCID: PMC10882511
- DOI: 10.1001/jamacardio.2023.5661
Effects of Pitavastatin on Coronary Artery Disease and Inflammatory Biomarkers in HIV: Mechanistic Substudy of the REPRIEVE Randomized Clinical Trial
Erratum in
-
Change to Open Access Status.JAMA Cardiol. 2024 May 1;9(5):487. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2024.0582. JAMA Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38416454 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Importance: Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is increased in people with HIV (PWH) and is characterized by premature noncalcified coronary plaque. In the Randomized Trial to Prevent Vascular Events in HIV (REPRIEVE), pitavastatin reduced major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) by 35% over a median of 5.1 years.
Objective: To investigate the effects of pitavastatin on noncalcified coronary artery plaque by coronary computed tomography angiography (CTA) and on inflammatory biomarkers as potential mechanisms for MACE prevention.
Design, setting, and participants: This double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial enrolled participants from April 2015 to February 2018 at 31 US clinical research sites. PWH without known CVD who were taking antiretroviral therapy and had low to moderate 10-year CVD risk were included. Data were analyzed from April to November 2023.
Intervention: Oral pitavastatin calcium, 4 mg per day.
Main outcomes and measures: Coronary CTA and inflammatory biomarkers at baseline and 24 months. The primary outcomes were change in noncalcified coronary plaque volume and progression of noncalcified plaque.
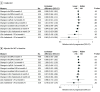
Results: Of 804 enrolled persons, 774 had at least 1 evaluable CTA. Plaque changes were assessed in 611 who completed both CT scans. Of 611 analyzed participants, 513 (84.0%) were male, the mean (SD) age was 51 (6) years, and the median (IQR) 10-year CVD risk was 4.5% (2.6-7.0). A total of 302 were included in the pitavastatin arm and 309 in the placebo arm. The mean noncalcified plaque volume decreased with pitavastatin compared with placebo (mean [SD] change, -1.7 [25.2] mm3 vs 2.6 [27.1] mm3; baseline adjusted difference, -4.3 mm3; 95% CI, -8.6 to -0.1; P = .04; 7% [95% CI, 1-12] greater reduction relative to placebo). A larger effect size was seen among the subgroup with plaque at baseline (-8.8 mm3 [95% CI, -17.9 to 0.4]). Progression of noncalcified plaque was 33% less likely with pitavastatin compared with placebo (relative risk, 0.67; 95% CI, 0.52-0.88; P = .003). Compared with placebo, the mean low-density lipoprotein cholesterol decreased with pitavastatin (mean change: pitavastatin, -28.5 mg/dL; 95% CI, -31.9 to -25.1; placebo, -0.8; 95% CI, -3.8 to 2.2). The pitavastatin arm had a reduction in both oxidized low-density lipoprotein (-29% [95% CI, -32 to -26] vs -13% [95% CI, -17 to -9]; P < .001) and lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (-7% [95% CI, -11 to -4] vs 14% [95% CI, 10-18]; P < .001) compared with placebo at 24 months.
Conclusions and relevance: In PWH at low to moderate CVD risk, 24 months of pitavastatin reduced noncalcified plaque volume and progression as well as markers of lipid oxidation and arterial inflammation. These changes may contribute to the observed MACE reduction in REPRIEVE.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02344290.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment on
-
Statins, Inflammation, and Tissue Context in REPRIEVE.JAMA Cardiol. 2024 Apr 1;9(4):334-335. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2023.5671. JAMA Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38381416 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- UM1 AI069494/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069424/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069456/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069470/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069439/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI157882/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL123339/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002384/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 HL164284/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 HL164285/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK040561/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI046386/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069412/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069470/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

