Partial Ligand Stripping from CsPbBr3 Nanocrystals Improves Their Performance in Light-Emitting Diodes
- PMID: 38381521
- PMCID: PMC11932522
- DOI: 10.1021/acsami.3c15201
Partial Ligand Stripping from CsPbBr3 Nanocrystals Improves Their Performance in Light-Emitting Diodes
Abstract
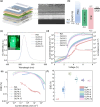
Halide perovskite nanocrystals (NCs), specifically CsPbBr3, have attracted considerable interest due to their remarkable optical properties for optoelectronic devices. To achieve high-efficiency light-emitting diodes (LEDs) based on CsPbBr3 nanocrystals (NCs), it is crucial to optimize both their photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) and carrier transport properties when they are deposited to form films on substrates. While the exchange of native ligands with didodecyl dimethylammonium bromide (DDAB) ligand pairs has been successful in boosting their PLQY, dense DDAB coverage on the surface of NCs should impede carrier transport and limit device efficiency. Following our previous work, here, we use oleyl phosphonic acid (OLPA) as a selective stripping agent to remove a fraction of DDAB from the NC surface and demonstrate that such stripping enhances carrier transport while maintaining a high PLQY. Through systematic optimization of OLPA dosage, we significantly improve the performance of CsPbBr3 LEDs, achieving a maximum external quantum efficiency (EQE) of 15.1% at 516 nm and a maximum brightness of 5931 cd m-2. These findings underscore the potential of controlled ligand stripping to enhance the performance of CsPbBr3 NC-based optoelectronic devices.
Keywords: CsPbBr3; carrier mobility; halide perovskites; light-emitting diodes; nanocrystal films; nanocrystals; surface ligands engineering.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Short-branched alkyl sulfobetaine-passivated CsPbBr3 nanocrystals for efficient green light emitting diodes.Nanoscale. 2024 Apr 18;16(15):7387-7395. doi: 10.1039/d4nr00965g. Nanoscale. 2024. PMID: 38545886
-
Stable Blue CsPbBr3 Perovskite Nanocrystals with Near-Unity Photoluminescence Quantum Yield by Surface Ligand Engineering.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025 Apr 30;17(17):25702-25712. doi: 10.1021/acsami.5c02501. Epub 2025 Apr 16. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025. PMID: 40241375
-
Complementary Triple-Ligand Engineering Approach to Methylamine Lead Bromide Nanocrystals for High-Performance Light-Emitting Diodes.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022 Mar 2;14(8):10508-10516. doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c18791. Epub 2022 Feb 18. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022. PMID: 35179027
-
Blue-Emitting CsPbBr3 Nanocrystals: Synthesis Progress and Bright Photoluminescence.Langmuir. 2025 Mar 11;41(9):5762-5781. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.4c05108. Epub 2025 Feb 26. Langmuir. 2025. PMID: 40008989 Review.
-
Colloidal FAPbBr3 perovskite nanocrystals for light emission: what's going on?J Mater Chem C Mater. 2022 Jun 9;10(37):13437-13461. doi: 10.1039/d2tc01373h. eCollection 2022 Sep 29. J Mater Chem C Mater. 2022. PMID: 36324302 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Blue CdSe/CdS core/crown nanoplatelet light-emitting diodes obtained via a design-of-experiments approach.Nanoscale. 2024 Dec 19;17(1):304-313. doi: 10.1039/d4nr03461a. Nanoscale. 2024. PMID: 39565594 Free PMC article.
-
Improving the Stability of Colloidal CsPbBr3 Nanocrystals with an Alkylphosphonium Bromide as Surface Ligand Pair.ACS Energy Lett. 2025 Apr 11;10(5):2268-2276. doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.5c00124. eCollection 2025 May 9. ACS Energy Lett. 2025. PMID: 40370949 Free PMC article.
-
Short-Wave Infrared Optoelectronics with Colloidal CdHgSe/ZnCdS Core/Shell Nanoplatelets.ACS Photonics. 2024 Dec 19;12(1):40-47. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.4c01944. eCollection 2025 Jan 15. ACS Photonics. 2024. PMID: 39830855 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dey A.; Ye J. Z.; De A.; Debroye E.; Ha S. K.; Bladt E.; Kshirsagar A. S.; Wang Z. Y.; Yin J.; Wang Y.; Quan L. N.; Yan F.; Gao M. Y.; Li X. M.; Shamsi J.; Debnath T.; Cao M. H.; Scheel M. A.; Kumar S.; Steele J. A.; Gerhard M.; Chouhan L.; Xu K.; Wu X. G.; Li Y. X.; Zhang Y. N.; Dutta A.; Han C.; Vincon I.; Rogach A. L.; Nag A.; Samanta A.; Korgel B. A.; Shih C. J.; Gamelin D. R.; Son D. H.; Zeng H. B.; Zhong H. Z.; Sun H. D.; Demir H. V.; Scheblykin I. G.; Mora-Seró I.; Stolarczyk J. K.; Zhang J. Z.; Feldmann J.; Hofkens J.; Luther J. M.; Pérez-Prieto J.; Li L.; Manna L.; Bodnarchuk M. I.; Kovalenko M. V.; Roeffaers M. B. J.; Pradhan N.; Mohammed O. F.; Bakr O. M.; Yang P. D.; Müller-Buschbaum P.; Kamat P. V.; Bao Q. L.; Zhang Q.; Krahne R.; Galian R. E.; Stranks S. D.; Bals S.; Biju V.; Tisdale W. A.; Yan Y.; Hoye R. L. Z.; Polavarapu L. State of the Art and Prospects for Halide Perovskite Nanocrystals. ACS Nano 2021, 15 (7), 10775–10981. 10.1021/acsnano.0c08903. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

