A handheld luminometer with sub-attomole limit of detection for distributed applications in global health
- PMID: 38381748
- PMCID: PMC10881016
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0002766
A handheld luminometer with sub-attomole limit of detection for distributed applications in global health
Abstract
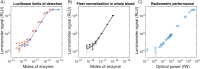
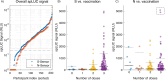
Luminescence is ubiquitous in biology research and medicine. Conceptually simple, the detection of luminescence nonetheless faces technical challenges because relevant signals can exhibit exceptionally low radiant power densities. Although low light detection is well-established in centralized laboratory settings, the cost, size, and environmental requirements of high-performance benchtop luminometers are not compatible with geographically-distributed global health studies or resource-constrained settings. Here we present the design and application of a ~$700 US handheld, battery-powered luminometer with performance on par with high-end benchtop instruments. By pairing robust and inexpensive Silicon Photomultiplier (SiPM) sensors with a low-profile shutter system, our design compensates for sensor non-idealities and thermal drift, achieving a limit of detection of 1.6E-19 moles of firefly luciferase. Using these devices, we performed two pilot cross-sectional serology studies to assess sars-cov-2 antibody levels: a cohort in the United States, as well as a field study in Bangladesh. Results from both studies were consistent with previous work and demonstrate the device's suitability for distributed applications in global health.
Copyright: © 2024 Lebel et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
S.E. declares a previously filed provisional patent application on the solution-based spLUC assay.
Figures



References
-
- El Mansouri B, Amarir F, Peyron F, Adlaoui EB, Piarroux R, Lykins J, et al. High performance of a novel point-of-care blood test for Toxoplasma infection in women from diverse regions of Morocco. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2021. Jan 1;10(1):1675–82. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2021.1948359 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Duchesne L, Hejblum G, Njouom R, Kane CT, d’Aquin Toni T, Moh R, et al. Model-based cost-effectiveness estimates of testing strategies for diagnosing hepatitis C virus infection in Central and Western Africa. PLOS ONE. 2020. Aug 24;15(8):e0238035. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0238035 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
