Discovery of a Cushing's syndrome protein kinase A mutant that biases signaling through type I AKAPs
- PMID: 38381834
- PMCID: PMC10881042
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adl1258
Discovery of a Cushing's syndrome protein kinase A mutant that biases signaling through type I AKAPs
Abstract
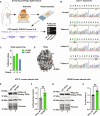
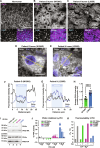
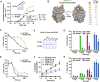
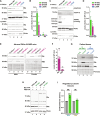
Adrenal Cushing's syndrome is a disease of cortisol hypersecretion often caused by mutations in protein kinase A catalytic subunit (PKAc). Using a personalized medicine screening platform, we discovered a Cushing's driver mutation, PKAc-W196G, in ~20% of patient samples analyzed. Proximity proteomics and photokinetic imaging reveal that PKAcW196G is unexpectedly distinct from other described Cushing's variants, exhibiting retained association with type I regulatory subunits (RI) and their corresponding A kinase anchoring proteins (AKAPs). Molecular dynamics simulations predict that substitution of tryptophan-196 with glycine creates a 653-cubic angstrom cleft between the catalytic core of PKAcW196G and type II regulatory subunits (RII), but only a 395-cubic angstrom cleft with RI. Endocrine measurements show that overexpression of RIα or redistribution of PKAcW196G via AKAP recruitment counteracts stress hormone overproduction. We conclude that a W196G mutation in the kinase catalytic core skews R subunit selectivity and biases AKAP association to drive Cushing's syndrome.
Figures


References
-
- Anton S. E., Kayser C., Maiellaro I., Nemec K., Möller J., Koschinski A., Zaccolo M., Annibale P., Falcke M., Lohse M. J., Bock A., Receptor-associated independent cAMP nanodomains mediate spatiotemporal specificity of GPCR signaling. Cell 185, 1130–1142.e11 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Bock A., Annibale P., Konrad C., Hannawacker A., Anton S. E., Maiellaro I., Zabel U., Sivaramakrishnan S., Falcke M., Lohse M. J., Optical mapping of cAMP signaling at the nanometer scale. Cell 184, 2793 (2021). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

