First-Line Nivolumab Plus Chemotherapy for Advanced Gastric, Gastroesophageal Junction, and Esophageal Adenocarcinoma: 3-Year Follow-Up of the Phase III CheckMate 649 Trial
- PMID: 38382001
- PMCID: PMC11185916
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.23.01601
First-Line Nivolumab Plus Chemotherapy for Advanced Gastric, Gastroesophageal Junction, and Esophageal Adenocarcinoma: 3-Year Follow-Up of the Phase III CheckMate 649 Trial
Abstract
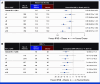
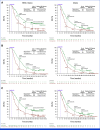
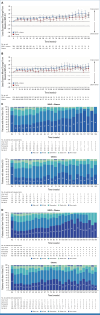
Clinical trials frequently include multiple end points that mature at different times. The initial report, typically based on the primary end point, may be published when key planned co-primary or secondary analyses are not yet available. Clinical Trial Updates provide an opportunity to disseminate additional results from studies, published in JCO or elsewhere, for which the primary end point has already been reported.We report 3-year efficacy and safety results from the phase III CheckMate 649 trial. Patients with previously untreated advanced or metastatic gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma were randomly assigned to nivolumab plus chemotherapy or chemotherapy. Primary end points were overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) by blinded independent central review (BICR) in patients whose tumors expressed PD-L1 combined positive score (CPS) ≥5. With 36.2-month minimum follow-up, for patients with PD-L1 CPS ≥5, the OS hazard ratio (HR) for nivolumab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy was 0.70 (95% CI, 0.61 to 0.81); 21% versus 10% of patients were alive at 36 months, respectively; the PFS HR was 0.70 (95% CI, 0.60 to 0.81); 36-month PFS rates were 13% versus 8%, respectively. The objective response rate (ORR) per BICR was 60% (95% CI, 55 to 65) with nivolumab plus chemotherapy versus 45% (95% CI, 40 to 50) with chemotherapy; median duration of response was 9.6 months (95% CI, 8.2 to 12.4) versus 7.0 months (95% CI, 5.6 to 7.9), respectively. Nivolumab plus chemotherapy also continued to show improvement in OS, PFS, and ORR versus chemotherapy in the overall population. Adding nivolumab to chemotherapy maintained clinically meaningful long-term survival benefit versus chemotherapy alone, with an acceptable safety profile, supporting the continued use of nivolumab plus chemotherapy as standard first-line treatment for advanced gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02872116.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures



References
-
- Elimova E, Wyrwicz L, Chen C, et al. : Health-related quality of life (HRQOL) in patients (pts) with advanced gastric cancer/gastroesophageal junction cancer (GC/GEJC) or esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC): 36-month results of nivolumab plus chemotherapy (N+C) versus (C) from CheckMate 649. J Clin Oncol 41, 2023. (suppl 16; abstr 4038) - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kato K, Sun J-M, Shah M, et al. : LBA8_PR Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy as first-line therapy in patients with advanced esophageal cancer: The phase 3 KEYNOTE-590 study. Ann Oncol 31:S1192-S1193, 2020. (suppl 4)
-
- Moehler MH, Kato K, Arkenau H-T, et al. : Rationale 305: Phase 3 study of tislelizumab plus chemotherapy vs placebo plus chemotherapy as first-line treatment (1L) of advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (GC/GEJC). J Clin Oncol 41, 2023. (suppl 4; abstr 286)
-
- Rha SY, Wyrwicz LS, Weber PEY, et al. : VP1-2023: Pembrolizumab (pembro) plus chemotherapy (chemo) as first-line therapy for advanced HER2-negative gastric or gastroesophageal junction (G/GEJ) cancer: Phase III KEYNOTE-859 study. Ann Oncol 34:319-320, 2023
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

