Highly accurate blood test for Alzheimer's disease is similar or superior to clinical cerebrospinal fluid tests
- PMID: 38382645
- PMCID: PMC11031399
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-024-02869-z
Highly accurate blood test for Alzheimer's disease is similar or superior to clinical cerebrospinal fluid tests
Abstract
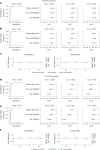
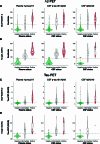
With the emergence of Alzheimer's disease (AD) disease-modifying therapies, identifying patients who could benefit from these treatments becomes critical. In this study, we evaluated whether a precise blood test could perform as well as established cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) tests in detecting amyloid-β (Aβ) plaques and tau tangles. Plasma %p-tau217 (ratio of phosporylated-tau217 to non-phosphorylated tau) was analyzed by mass spectrometry in the Swedish BioFINDER-2 cohort (n = 1,422) and the US Charles F. and Joanne Knight Alzheimer Disease Research Center (Knight ADRC) cohort (n = 337). Matched CSF samples were analyzed with clinically used and FDA-approved automated immunoassays for Aβ42/40 and p-tau181/Aβ42. The primary and secondary outcomes were detection of brain Aβ or tau pathology, respectively, using positron emission tomography (PET) imaging as the reference standard. Main analyses were focused on individuals with cognitive impairment (mild cognitive impairment and mild dementia), which is the target population for available disease-modifying treatments. Plasma %p-tau217 was clinically equivalent to FDA-approved CSF tests in classifying Aβ PET status, with an area under the curve (AUC) for both between 0.95 and 0.97. Plasma %p-tau217 was generally superior to CSF tests in classification of tau-PET with AUCs of 0.95-0.98. In cognitively impaired subcohorts (BioFINDER-2: n = 720; Knight ADRC: n = 50), plasma %p-tau217 had an accuracy, a positive predictive value and a negative predictive value of 89-90% for Aβ PET and 87-88% for tau PET status, which was clinically equivalent to CSF tests, further improving to 95% using a two-cutoffs approach. Blood plasma %p-tau217 demonstrated performance that was clinically equivalent or superior to clinically used FDA-approved CSF tests in the detection of AD pathology. Use of high-performance blood tests in clinical practice can improve access to accurate AD diagnosis and AD-specific treatments.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
N.R.B. and R.J.B. are co-inventors on US patent applications: ‘Methods to detect novel tau species in CSF and use thereof to track tau neuropathology in Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies’ and ‘CSF phosphorylated tau and amyloid beta profiles as biomarkers of tauopathies’. N.R.B. and R.J.B. are co-inventors on a non-provisional patent application: ‘Methods of diagnosing and treating based on site-specific tau phosphorylation’. S.E.S. served on a scientific advisory board for Eisai. T.L.S.B. has investigator-initiated research funding from the National Institutes of Health, the Alzheimer’s Association, the Barnes-Jewish Hospital Foundation and Siemens. She participates as a site investigator in clinical trials sponsored by Avid Radiopharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly, Biogen, Eisai, Janssen and Roche. She also serves as a consultant to Biogen, Eli Lilly, Eisai and Siemens. Neither J.C.M. nor his family owns stock or has equity interest (outside of mutual funds or other externally directed accounts) in any pharmaceutical or biotechnology company. O.H. has acquired research support (for the institution) from ADx, Avid Radiopharmaceuticals, Biogen, C2N Diagnostics, Eli Lilly, Eisai, Fujirebio, GE Healthcare, Pfizer and Roche. In the past 2 years, he has received consultancy/speaker fees from AC Immune, Alzpath, BioArctic, Biogen, Bristol Meyer Squibb, Cerveau, Eisai, Fujirebio, Genentech, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Roche and Siemens. R.J.B. co-founded C2N Diagnostics. Washington University and R.J.B. have equity ownership interest in C2N Diagnostics and receive royalty income based on technology (stable isotope labeling kinetics, blood plasma assay and methods of diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease with phosphorylation changes) that is licensed by Washington University to C2N Diagnostics. R.J.B. receives income from C2N Diagnostics for serving on the scientific advisory board. R.J.B. has received research funding from Avid Radiopharmaceuticals, Janssen, Roche/Genentech, Eli Lilly, Eisai, Biogen, AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb and Novartis. O.H. has acquired research support (for the institution) from ADx, Avid Radiopharmaceuticals, Biogen, C2N Diagnostics, Eli Lilly, Eisai, Fujirebio, GE Healthcare, Pfizer and Roche. In the past 2 years, he has received consultancy/speaker fees from AC Immune, Alzpath, BioArctic, Biogen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Cerveau, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Fujirebio, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Roche, Sanofi and Siemens. S.P. has acquired research support (for the institution) from ki:elements / Alzheimerʼs Drug Discovery Foundation. In the past 2 years, he has received consultancy/speaker fees from BioArtic, Biogen, Eli Lilly and Roche. L.E.C. has received research support from GE Healthcare (paid to institution). G.D.R. has received research support from Avid Radiopharmaceuiticals, GE Healthcare, Life Molecular Imaging and Genentech and consulting fees from Alector, Eli Lilly, Johnson & Johnson and Merck and serves as Associate Editor for J
Figures




References
-
- Alzheimerʼs Disease International. World Alzheimer Report: The Global Impact of Dementia. https://www.alzint.org/u/WorldAlzheimerReport2015.pdf (2015).

