Phase separation-mediated biomolecular condensates and their relationship to tumor
- PMID: 38383403
- PMCID: PMC10880379
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-024-01518-9
Phase separation-mediated biomolecular condensates and their relationship to tumor
Abstract
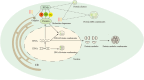
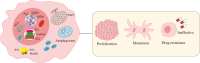
Phase separation is a cellular phenomenon where macromolecules aggregate or segregate, giving rise to biomolecular condensates resembling "droplets" and forming distinct, membrane-free compartments. This process is pervasive in biological cells, contributing to various essential cellular functions. However, when phase separation goes awry, leading to abnormal molecular aggregation, it can become a driving factor in the development of diseases, including tumor. Recent investigations have unveiled the intricate connection between dysregulated phase separation and tumor pathogenesis, highlighting its potential as a novel therapeutic target. This article provides an overview of recent phase separation research, with a particular emphasis on its role in tumor, its therapeutic implications, and outlines avenues for further exploration in this intriguing field.
Keywords: Biomolecular condensates; Phase separation; Therapeutic targets; Tumor.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lactylation-regulated biomolecular condensates: metabolic control of phase separation in physiology and disease.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 May 25;23(1):239. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02244-6. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 40414883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Burgeoning Significance of Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation in the Pathogenesis and Therapeutics of Cancers.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Feb 12;20(5):1652-1668. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.92988. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38481812 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peptide-Based Biomimetic Condensates via Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation as Biomedical Delivery Vehicles.Biomacromolecules. 2024 Sep 9;25(9):5468-5488. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.4c00814. Epub 2024 Aug 23. Biomacromolecules. 2024. PMID: 39178343 Review.
-
Phase separation drives the formation of biomolecular condensates in the immune system.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 10;13:986589. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.986589. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36439121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Demixing is a default process for biological condensates formed via phase separation.Science. 2024 May 24;384(6698):920-928. doi: 10.1126/science.adj7066. Epub 2024 May 23. Science. 2024. PMID: 38781377
Cited by
-
Spontaneous Self-Organized Order Emerging From Intrinsically Disordered Protein Polymers.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2025 Jan-Feb;17(1):e70003. doi: 10.1002/wnan.70003. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2025. PMID: 39950263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lactylation-regulated biomolecular condensates: metabolic control of phase separation in physiology and disease.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 May 25;23(1):239. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02244-6. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 40414883 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Olins DE, Olins AL. Chromatin history: our view from the bridge. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4(10):809–814. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

