ZSWIM4 inhibition improves chemosensitivity in epithelial ovarian cancer cells by suppressing intracellular glycine biosynthesis
- PMID: 38383406
- PMCID: PMC10880229
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-024-04980-8
ZSWIM4 inhibition improves chemosensitivity in epithelial ovarian cancer cells by suppressing intracellular glycine biosynthesis
Abstract
Background: Zinc finger SWIM-type containing 4 (ZSWIM4) induces drug resistance in breast cancer cells. However, its role in epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) remains unknown. In this study, we aimed to investigate the clinical significance of ZSWIM4 expression in EOC and develop new clinical therapeutic strategies for EOC.
Methods: ZSWIM4 expression in control and EOC tumor tissues was examined using immunohistochemistry. Lentiviral transduction, Cell Counting Kit-8 assay, tumorsphere formation assay, flow cytometry, western blotting, and animal xenograft model were used to assess the role of ZSWIM4 in chemotherapy. Cleavage Under Targets and Tagmentation (CUT&Tag) assays, chromatin immunoprecipitation assays, and luciferase reporter assays were used to confirm FOXK1-mediated upregulation of ZSWIM4 expression. The mechanism by which ZSWIM4 inhibition improves chemosensitivity was evaluated using RNA-sequencing. A ZSWIM4-targeting inhibitor was explored by virtual screening and surface plasmon resonance analysis. Patient-derived organoid (PDO) models were constructed from EOC tumor tissues with ZSWIM4 expression.
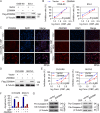
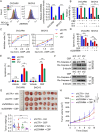
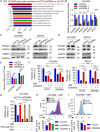
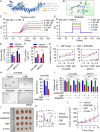
Results: ZSWIM4 was overexpressed in EOC tumor tissues and impaired patient prognoses. Its expression correlated positively with EOC recurrence. ZSWIM4 expression was upregulated following carboplatin treatment, which, in turn, contributed to chemoresistance. Silencing ZSWIM4 expression sensitized EOC cells to carboplatin treatment in vitro and in vivo. FOXK1 could bind to the GTAAACA sequence of the ZSWIM4 promoter region to upregulate ZSWIM4 transcriptional activity and FOXK1 expression increased following carboplatin treatment, leading to an increase in ZSWIM4 expression. Mechanistically, ZSWIM4 knockdown downregulated the expression of several rate-limiting enzymes involved in glycine synthesis, causing a decrease in intracellular glycine levels, thus enhancing intracellular reactive oxygen species production induced by carboplatin treatment. Compound IPN60090 directly bound to ZSWIM4 protein and exerted a significant chemosensitizing effect in both EOC cells and PDO models.
Conclusions: ZSWIM4 inhibition enhanced EOC cell chemosensitivity by ameliorating intracellular glycine metabolism reprogramming, thus providing a new potential therapeutic strategy for EOC.
Keywords: Carboplatin; Chemosensitivity; Epithelial ovarian cancer; FOXK1; Glycine biosynthesis; ZSWIM4.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of this article.
Figures




Similar articles
-
High ATP6V1B1 expression is associated with poor prognosis and platinum‑based chemotherapy resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer.Oncol Rep. 2023 May;49(5):102. doi: 10.3892/or.2023.8539. Epub 2023 Mar 31. Oncol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36999629 Free PMC article.
-
Aurora-A/SOX8/FOXK1 signaling axis promotes chemoresistance via suppression of cell senescence and induction of glucose metabolism in ovarian cancer organoids and cells.Theranostics. 2020 May 25;10(15):6928-6945. doi: 10.7150/thno.43811. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32550913 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA‑320 targets mitogen‑activated protein kinase 1 to inhibit cell proliferation and invasion in epithelial ovarian cancer.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Dec;16(6):8530-8536. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7664. Epub 2017 Sep 29. Mol Med Rep. 2017. Retraction in: Mol Med Rep. 2024 Mar;29(3):45. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13169. PMID: 28990044 Retracted.
-
Spotlight on New Hallmarks of Drug-Resistance towards Personalized Care for Epithelial Ovarian Cancer.Cells. 2024 Mar 31;13(7):611. doi: 10.3390/cells13070611. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38607050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Treatment.Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2018 Jul;28(6):1085-1089. doi: 10.1097/IGC.0000000000001269. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29727350 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphocholine inhibits proliferation and reduces stemness of endometrial cancer cells by downregulating mTOR-c-Myc signaling.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Dec 16;82(1):3. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05517-4. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39680126 Free PMC article.
-
Organoids research progress in gynecological cancers: a bibliometric analysis.Front Oncol. 2024 Oct 28;14:1484074. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1484074. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39529835 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

