To allow or avoid pain during shoulder rehabilitation exercises for patients with chronic rotator cuff tendinopathy-Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial (the PASE trial)
- PMID: 38383459
- PMCID: PMC10880378
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-024-07973-6
To allow or avoid pain during shoulder rehabilitation exercises for patients with chronic rotator cuff tendinopathy-Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial (the PASE trial)
Abstract
Background: Rotator cuff (RC) tendinopathy is the most reported shoulder disorder in the general population with highest prevalence in overhead athletes and adult working-age population. A growing body of evidence support exercise therapy as an effective intervention, but to date there are no prospective randomized controlled trials addressing pain as an intervention variable.
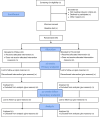
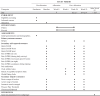
Methods: A single-site, prospective, pragmatic, assessor-blinded randomized controlled superiority trial. Eighty-four patients aged 18-55 years with chronic (symptom duration over 3 months) RC tendinopathy are randomized 1:1 to receive shoulder exercise during which pain is either allowed or avoided. The intervention period lasts 26 weeks. During that period, participants in both groups are offered 8 individual on-site sessions with an assigned sports physiotherapist. Participants perform home exercises and are provided with a pain and exercise logbook and asked to report completed home-based exercise sessions and reasons for not completing sessions (pain or other reasons). Patients are also asked to report load and the number of sets and repetitions per sets for each exercise session. The logbooks are collected continuously throughout the intervention period. The primary and secondary outcomes are obtained at baseline, 6 weeks, 26 weeks, and 1 year after baseline. The primary outcome is patient-reported pain and disability using the Shoulder PAin and Disability Index (SPADI). Secondary outcomes are patient-reported pain and disability using Disability Arm Shoulder and Hand short-form (Quick DASH), and shoulder pain using Numeric Pain Rating Scale. Objective outcomes are shoulder range of motion, isometric shoulder muscle strength, pain sensitivity, working ability, and structural changes in the supraspinatus tendon and muscle using ultrasound.
Discussion: The results of this study will contribute knowledge about the treatment strategies for patients with RC tendinopathy and help physiotherapists in clinical decision-making. This is the first randomized controlled trial comparing the effects of allowing pain versus avoiding pain during shoulder exercises in patients with chronic RC tendinopathy. If tolerating pain during and after exercise proves to be effective, it will potentially expand our understanding of "exercising into pain" for this patient group, as there is currently no consensus.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT05124769. Registered on August 11, 2021.
Keywords: Exercise; Pain; Rehabilitation; Rotator cuff tendinopathy; SPADI; Shoulder; Strength.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Isometric versus isotonic exercise in individuals with rotator cuff tendinopathy-Effects on shoulder pain, functioning, muscle strength, and electromyographic activity: A protocol for randomized clinical trial.PLoS One. 2023 Nov 13;18(11):e0293457. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0293457. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37956135 Free PMC article.
-
The Effectiveness of an Upper Extremity Neuromuscular Training Program on the Shoulder Function of Military Members With a Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial.Mil Med. 2019 May 1;184(5-6):e385-e393. doi: 10.1093/milmed/usy294. Mil Med. 2019. PMID: 30423137 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Do therapeutic exercises impact supraspinatus tendon thickness? Secondary analyses of the combined dataset from two randomized controlled trials in patients with rotator cuff-related shoulder pain.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2024 Sep;33(9):1918-1927. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2024.03.055. Epub 2024 May 16. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2024. PMID: 38762149
-
Surgery for rotator cuff tears.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Dec 9;12(12):CD013502. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013502. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31813166 Free PMC article.
-
Subacromial decompression surgery for rotator cuff disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Jan 17;1(1):CD005619. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005619.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 30707445 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Luime JJ, Koes BW, Hendriksen IJ, Burdorf A, Verhagen AP, Miedema HS, et al. Prevalence and incidence of shoulder pain in the general population; a systematic review. Scand J Rheumatol. 2004;33(2):73–81. - PubMed
-
- Lewis JS. Rotator cuff tendinopathy/subacromial impingement syndrome: is it time for a new method of assessment? Br J Sports Med. 2009;43(4):259–264. - PubMed
-
- Malliaras P, Johnston R, Street G, Littlewood C, Bennell K, Haines T, et al. The efficacy of higher versus lower dose exercise in rotator cuff tendinopathy: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2020;101(10):1822–1834. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

