Kallistatin deficiency exacerbates neuronal damage after cardiac arrest
- PMID: 38383562
- PMCID: PMC10881987
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-54415-z
Kallistatin deficiency exacerbates neuronal damage after cardiac arrest
Abstract
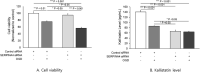
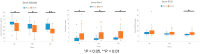
The purpose of study was to evaluate that kallistatin deficiency causes excessive production of reactive oxygen species and exacerbates neuronal injury after cardiac arrest. For in vitro study, kallistatin knockdown human neuronal cells were given ischemia-reperfusion injury, and the oxidative stress and apoptosis were evaluated. For clinical study, cardiac arrest survivors admitted to the ICU were divided into the good (CPC 1-2) and poor (CPC 3-5) 6-month neurological outcome groups. The serum level of kallistatin, Nox-1, H2O2 were measured. Nox-1 and H2O2 levels were increased in the kallistatin knockdown human neuronal cells with ischemia-reperfusion injury (p < 0.001) and caspase-3 was elevated and apoptosis was promoted (SERPINA4 siRNA: p < 0.01). Among a total of 62 cardiac arrest survivors (16 good, 46 poor), serum kallistatin were lower, and Nox-1 were higher in the poor neurological group at all time points after admission to the ICU (p = 0.013 at admission; p = 0.020 at 24 h; p = 0.011 at 72 h). At 72 h, H2O2 were higher in the poor neurological group (p = 0.038). Kallistatin deficiency exacerbates neuronal ischemia-reperfusion injury and low serum kallistatin levels were associated with poor neurological outcomes in cardiac arrest survivors.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Low serum Kallistatin level was associated with poor neurological outcome of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest survivors: Proteomics study.Resuscitation. 2018 Jul;128:6-10. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2018.04.025. Epub 2018 Apr 23. Resuscitation. 2018. PMID: 29698750
-
Protective role of kallistatin in oxygen-glucose deprivation and reoxygenation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.Clin Exp Emerg Med. 2024 Mar;11(1):43-50. doi: 10.15441/ceem.23.106. Epub 2024 Mar 21. Clin Exp Emerg Med. 2024. PMID: 38204159 Free PMC article.
-
Novel role of kallistatin in protection against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by preventing apoptosis and inflammation.Hum Gene Ther. 2006 Dec;17(12):1201-13. doi: 10.1089/hum.2006.17.1201. Hum Gene Ther. 2006. PMID: 17081080
-
Kallistatin: double-edged role in angiogenesis, apoptosis and oxidative stress.Biol Chem. 2017 Nov 27;398(12):1309-1317. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2017-0180. Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28742513 Review.
-
Protective Role of Endogenous Kallistatin in Vascular Injury and Senescence by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Inflammation.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Dec 2;2018:4138560. doi: 10.1155/2018/4138560. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 30622668 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association between SIRT-1 and SERPINA4 gene polymorphisms and the risk of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome among Egyptian children.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 May 22;52(1):493. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10568-2. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40402303
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

