Cortical astrocyte N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors influence whisker barrel activity and sensory discrimination in mice
- PMID: 38383567
- PMCID: PMC10882001
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-45989-3
Cortical astrocyte N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors influence whisker barrel activity and sensory discrimination in mice
Abstract
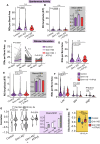
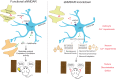
Astrocytes express ionotropic receptors, including N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs). However, the contribution of NMDARs to astrocyte-neuron interactions, particularly in vivo, has not been elucidated. Here we show that a knockdown approach to selectively reduce NMDARs in mouse cortical astrocytes decreases astrocyte Ca2+ transients evoked by sensory stimulation. Astrocyte NMDAR knockdown also impairs nearby neuronal circuits by elevating spontaneous neuron activity and limiting neuronal recruitment, synchronization, and adaptation during sensory stimulation. Furthermore, this compromises the optimal processing of sensory information since the sensory acuity of the mice is reduced during a whisker-dependent tactile discrimination task. Lastly, we rescue the effects of astrocyte NMDAR knockdown on neurons and improve the tactile acuity of the animal by supplying exogenous ATP. Overall, our findings show that astrocytes can respond to nearby neuronal activity via their NMDAR, and that these receptors are an important component for purinergic signaling that regulate astrocyte-neuron interactions and cortical sensory discrimination in vivo.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Functional significance of cortical NMDA receptors in somatosensory information processing.J Neurophysiol. 2013 Dec;110(11):2627-36. doi: 10.1152/jn.00052.2013. Epub 2013 Sep 18. J Neurophysiol. 2013. PMID: 24047907 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocyte β-Adrenergic Receptor Activity Regulates NMDA Receptor Signaling of Medial Prefrontal Cortex Pyramidal Neurons.J Neurosci. 2024 Jan 10;44(2):e0990232023. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0990-23.2023. J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 37989594 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocyte calcium signaling transforms cholinergic modulation to cortical plasticity in vivo.J Neurosci. 2011 Dec 7;31(49):18155-65. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5289-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22159127 Free PMC article.
-
NMDA Receptors in Astrocytes: In Search for Roles in Neurotransmission and Astrocytic Homeostasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 14;20(2):309. doi: 10.3390/ijms20020309. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30646531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Astrocytic NMDA Receptors.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2024 Jun;89(6):1045-1060. doi: 10.1134/S0006297924060063. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2024. PMID: 38981700 Review.
Cited by
-
N-methyl-D-aspartate Receptors and Depression: Linking Psychopharmacology, Pathology and Physiology in a Unifying Hypothesis for the Epigenetic Code of Neural Plasticity.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Nov 30;17(12):1618. doi: 10.3390/ph17121618. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39770460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NMDA Receptors Coordinate Metabolic Reprogramming and Mitophagy in Schwann Cells to Promote Peripheral Nerve Regeneration.Research (Wash D C). 2025 Aug 5;8:0825. doi: 10.34133/research.0825. eCollection 2025. Research (Wash D C). 2025. PMID: 40766001 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocytic G Protein-Coupled Receptors in Drug Addiction.Engineering (Beijing). 2025 Jan;44:256-265. doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2024.12.016. Epub 2024 Dec 25. Engineering (Beijing). 2025. PMID: 40109668 Free PMC article.
-
A spatial threshold for astrocyte calcium surge.Elife. 2024 Dec 16;12:RP90046. doi: 10.7554/eLife.90046. Elife. 2024. PMID: 39680037 Free PMC article.
-
Rethinking Sensory Information Processing: The Essential Role of Astrocytes.J Neurochem. 2025 Jun;169(6):e70113. doi: 10.1111/jnc.70113. J Neurochem. 2025. PMID: 40490971 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

