Plasma metabolomic differences in early-onset compared to average-onset colorectal cancer
- PMID: 38383634
- PMCID: PMC10881959
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-54560-5
Plasma metabolomic differences in early-onset compared to average-onset colorectal cancer
Abstract
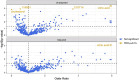
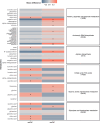
Deleterious effects of environmental exposures may contribute to the rising incidence of early-onset colorectal cancer (eoCRC). We assessed the metabolomic differences between patients with eoCRC, average-onset CRC (aoCRC), and non-CRC controls, to understand pathogenic mechanisms. Patients with stage I-IV CRC and non-CRC controls were categorized based on age ≤ 50 years (eoCRC or young non-CRC controls) or ≥ 60 years (aoCRC or older non-CRC controls). Differential metabolite abundance and metabolic pathway analyses were performed on plasma samples. Multivariate Cox proportional hazards modeling was used for survival analyses. All P values were adjusted for multiple testing (false discovery rate, FDR P < 0.15 considered significant). The study population comprised 170 patients with CRC (66 eoCRC and 104 aoCRC) and 49 non-CRC controls (34 young and 15 older). Citrate was differentially abundant in aoCRC vs. eoCRC in adjusted analysis (Odds Ratio = 21.8, FDR P = 0.04). Metabolic pathways altered in patients with aoCRC versus eoCRC included arginine biosynthesis, FDR P = 0.02; glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism, FDR P = 0.005; citrate cycle, FDR P = 0.04; alanine, aspartate, and glutamate metabolism, FDR P = 0.01; glycine, serine, and threonine metabolism, FDR P = 0.14; and amino-acid t-RNA biosynthesis, FDR P = 0.01. 4-hydroxyhippuric acid was significantly associated with overall survival in all patients with CRC (Hazards ratio, HR = 0.4, 95% CI 0.3-0.7, FDR P = 0.05). We identified several unique metabolic alterations, particularly the significant differential abundance of citrate in aoCRC versus eoCRC. Arginine biosynthesis was the most enriched by the differentially altered metabolites. The findings hold promise in developing strategies for early detection and novel therapies.
Keywords: Arginine biosynthesis pathway; Citric acid cycle; Early onset colorectal cancer; Metabolomics; Pathway analysis; Synthetic lethality; Translational research.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Thejus Jayakrishnan – No disclosures Nicole Farha – No disclosures Arshiya Mariam – No disclosures Daniel M. Rotroff – Equity stake in Clarified Precision Medicine, LLC. Received research support from Novo Nordisk, consulting honoraria from Pharmazaam, LLC, and Interpares Biomedicine owns intellectual property related to the detection of type-2 diabetes, chronic liver disease, and liver cancer Federico Aucejo – No disclosures Shimoli V. Barot – No disclosures Madison Conces – No disclosures Kanika G. Nair – No disclosures Smitha S. Krishnamurthi -- Consulting or Advisory Role––Array BioPharma, Research funding- Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Aravive, Natera Stephanie L. Schmit – No disclosures David Liska – Consulting or Advisory Role- Olympus Medical Systems, Research funding – Merck, Freenome Suneel D. Kamath – Consulting or advisory role: Exelixis, Guardant Health. Tempus, SeaGen, Foundation Medicine. Alok A. Khorana has been paid honoraria - Janssen, Sanofi, BMS, Anthos, Pfizer, Bayer, Nektar, and Medscape. Consulting or advisory role: Janssen, Sanofi, BMS, Anthos, Pfizer, Bayer, Nektar, and Medscape
Figures



References
-
- Cancer of the Colon and Rectum - Cancer Stat Facts. SEER. Accessed December 1, 2019. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/colorect.html
-
- Final Recommendation Statement: Screening for Colorectal Cancer|United States Preventive Services Taskforce. Accessed March 3, 2023. https://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/announcements/final...
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

