TRAIL predisposes non-small cell lung cancer to ferroptosis by regulating ASK-1/JNK1 pathway
- PMID: 38383815
- PMCID: PMC10881944
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-024-00890-9
TRAIL predisposes non-small cell lung cancer to ferroptosis by regulating ASK-1/JNK1 pathway
Abstract
Objective: Our current study aimed to assess the relationship between TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) and ferroptosis in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) development.
Methods: The expression of TRAIL was detected by western blot, RT-qRCR and immunohistochemistry. The viability of NSCLC cells was analyzed by CCK-8 kit. The migration and invasion of NSCLC cells were detected by wound healing assay and transwell assay, respectively. Labile iron pool (LIP) was detected based on the calcein-acetoxymethyl ester method. Ferrous iron (Fe2+) and iron levels were assessed by detection kits. The levels of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and malondialdehyde (MDA) were measured using corresponding detection kits. Mice tumor xenograft models were used for the in vivo research.
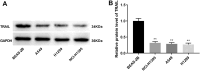
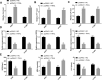
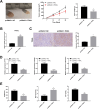
Results: The expression of TRAIL was reduced in H1299, NCL-H1395, and A549 cells compared with BEAS-2B cells. The up-regulation of TRAIL expression significantly reduced cell viability, invasion, and migration of H1299 and A549 cells. TRAIL reduced the expression of ferroptosis-related genes (FTH1, GPX4, and SLC7A11), increased the levels of LIP, iron, and Fe2+, and promoted lipid peroxidation, thereby predisposing NSCLC cells to ferroptosis. TRAIL up-regulated the expression of phosphate modification of ASK-1 and JNK. ASKI-1 inhibitor GS-4977 attenuated the effects of TRAIL on the viability, migration, invasion, and ferroptosis of H1299 cells. Furthermore, TRAIL further suppressed tumor growth and ferroptosis in mice tumor xenograft models.
Conclusion: We indicated that overexpression of TRAIL induced ferroptosis in NSCLC cells and exerted anti-tumor effects. Mechanistically, TRAIL promoted ferroptosis by the activation of the ASK-1/JNK1 pathway. Our results may provide new therapeutic strategies for NSCLC.
Keywords: ASK-1/JNK1 pathway; Ferroptosis; NSCLC; TRAIL.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Curcumin induces ferroptosis in non-small-cell lung cancer via activating autophagy.Thorac Cancer. 2021 Apr;12(8):1219-1230. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13904. Epub 2021 Mar 3. Thorac Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33656766 Free PMC article.
-
HIF‑1α inhibits ferroptosis and promotes malignant progression in non‑small cell lung cancer by activating the Hippo‑YAP signalling pathway.Oncol Lett. 2023 Jan 19;25(3):90. doi: 10.3892/ol.2023.13676. eCollection 2023 Mar. Oncol Lett. 2023. PMID: 36817050 Free PMC article.
-
RBM15 silencing promotes ferroptosis by regulating the TGF-β/Smad2 pathway in lung cancer.Environ Toxicol. 2023 Mar;38(4):950-961. doi: 10.1002/tox.23741. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Environ Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 36715115
-
Effects of ebv-miR-BART7 on tumorigenicity, metastasis, and TRAIL sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Jun;120(6):10057-10068. doi: 10.1002/jcb.28289. Epub 2018 Dec 19. J Cell Biochem. 2019. Retraction in: J Cell Biochem. 2021 Nov;122 Suppl 1:S125. doi: 10.1002/jcb.30105. PMID: 30569505 Retracted.
-
Induction of ferroptosis by natural products in non-small cell lung cancer: a comprehensive systematic review.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 1;15:1385565. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1385565. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38751790 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gamie Z, Kapriniotis K, Papanikolaou D, Haagensen E, Da Conceicao Ribeiro R, Dalgarno K, Krippner-Heidenreich A, Gerrand C, Tsiridis E, Rankin KS. TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) for bone sarcoma treatment: pre-clinical and clinical data. Cancer Lett. 2017;409:66–80. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.08.036. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
