Soluble guanylate cyclase stimulators and activators: new horizons in the treatment of priapism associated with sickle cell disease
- PMID: 38384294
- PMCID: PMC10879333
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1357176
Soluble guanylate cyclase stimulators and activators: new horizons in the treatment of priapism associated with sickle cell disease
Abstract
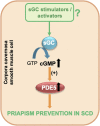
Priapism, defined as a prolonged and often painful penile erection occurring without sexual stimulation or desire, is a common complication in sickle cell disease (SCD), affecting up to 48% of male patients. This condition presents significant clinical challenges and can lead to erectile dysfunction if not properly managed. Current pharmacological treatments for SCD-related priapism are primarily reactive rather than preventative, highlighting a gap in effective medical intervention strategies. A critical factor in developing priapism is the reduced basal bioavailability of nitric oxide (NO) and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) in erectile tissues. New prevention strategies should ideally target the underlying pathophysiology of the disease. Compounds that stimulate and activate soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) emerge as potential therapeutic candidates since these compounds have the property of inducing cGMP production by sGC. This review explores the potential of sGC stimulators and activators in treating priapism associated with SCD. We discuss the advantages of these agents in the face of the challenging pathophysiology of SCD. Additionally, the review underscores the impact of intravascular hemolysis and oxidative stress on priapism pathophysiology in SCD, areas in which sGC stimulators and activators may also have beneficial therapeutic effects.
Keywords: anemia; cGMP; corpus cavernosum; erectile dysfunction; nitric oxide.
Copyright © 2024 Pereira, Silveira, Calmasini and Silva.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nitric Oxide Resistance in Priapism Associated with Sickle Cell Disease: Mechanisms, Therapeutic Challenges, and Future Directions.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2024 Jul 18;390(2):203-212. doi: 10.1124/jpet.123.001962. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2024. PMID: 38262744 Review.
-
Targeting heme in sickle cell disease: new perspectives on priapism treatment.Front Physiol. 2024 Jul 17;15:1435220. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1435220. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39086934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Erectile Dysfunction in Heme-Deficient Nitric Oxide-Unresponsive Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Knock-In Mice.J Sex Med. 2017 Feb;14(2):196-204. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2016.12.007. J Sex Med. 2017. PMID: 28161078
-
Heme-induced corpus cavernosum relaxation and its implications for priapism in sickle cell disease: a mechanistic insight.Andrology. 2024 Nov;12(8):1857-1864. doi: 10.1111/andr.13599. Epub 2024 Jan 17. Andrology. 2024. PMID: 38231174
-
Modulation of soluble guanylate cyclase for the treatment of erectile dysfunction.Physiology (Bethesda). 2013 Jul;28(4):262-9. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00001.2013. Physiology (Bethesda). 2013. PMID: 23817801 Review.
Cited by
-
Omega-3 fatty acids improves tamoxifen-induced sexual dysfunction in male Wistar rats by modulating NO/cGMP signaling and monoamine neurotransmitters activities.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2025 Jun 18. doi: 10.1007/s00213-025-06836-5. Online ahead of print. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2025. PMID: 40528104
References
-
- Alexandre E. C., Leiria L. O., Silva F. H., Mendes-Silvério C. B., Calmasini F. B., Davel A. P. C., et al. (2014). Soluble guanylyl cyclase (sGC) degradation and impairment of nitric oxide-mediated responses in urethra from obese mice: reversal by the sGC activator BAY 60-2770. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 349, 2–9. 10.1124/jpet.113.211029 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alvaia M. A., Maia H. A. A. da S., Nelli A. de M., Guimarães C. O. S., Carvalho E. S. de S., Netto J. M. B., et al. (2020). Prevalence of priapism in individuals with sickle cell disease and implications on male sexual function. Einstein Sao Paulo Braz 18, eAO5070. 10.31744/einstein_journal/2020AO5070 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

