The FTO Mediated N6-Methyladenosine Modification of DDIT4 Regulation with Tumorigenesis and Metastasis in Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 38384328
- PMCID: PMC10879844
- DOI: 10.34133/research.0313
The FTO Mediated N6-Methyladenosine Modification of DDIT4 Regulation with Tumorigenesis and Metastasis in Prostate Cancer
Abstract
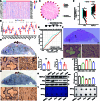
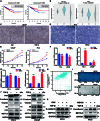
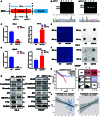
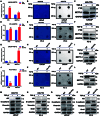
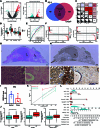
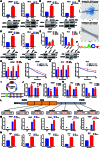
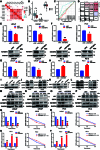
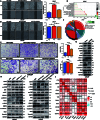
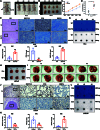
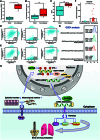
The progression of numerous malignancies has been linked to N6-methyladenosine (m6A) alteration. However, the opposite trend of m6A levels in the development and metastasis of cancer has not been reported. This study aimed to evaluate the biological function and mechanism of fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) in regulating m6A modification in prostate cancer development and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). An EMT model of LNCaP and PC-3 cells was established with transforming growth factor-β treatment, and FTO knockout cell line was established in prostate cancer cells using the CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing technology. The level of m6A modification in tumor tissues was higher than that in normal prostate tissues; m6A levels were decreased after EMT. FTO deletion increased m6A expression and enhanced PC-3 cell motility, invasion, and EMT both in vitro and in vivo. RNA sequencing and functional investigations suggested that DDIT4, a novel EMT target gene, plays a role in m6A-regulated EMT, which was recognized and stabilized by the m6A effector IGF2BP2/3. Decreased FTO expression was an independent indicator of worse survival, and the level of DDIT4 was considerably elevated in patients with bone metastasis. Thus, this study revealed that the m6A demethylase FTO can play different roles in prostate cancer as a regulator of EMT and an inhibitor of m6A modification. Moreover, DDIT4 can be suggested as a possible biomarker for prostate cancer metastasis prediction.
Copyright © 2024 Yue Zhao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72(1):7–33. - PubMed
-
- Potosky AL, Miller BA, Albertsen PC, Kramer BS. The role of increasing detection in the rising incidence of prostate cancer. JAMA. 1995;273(7):548–552. - PubMed
-
- Liotta LA. Tumor invasion and metastases-role of the extracellular matrix: Rhoads memorial award lecture. Cancer Res. 1986;46(1):1–7. - PubMed
-
- Heinlein CA, Chang C. Androgen receptor in prostate cancer. Endocr Rev. 2004;25(2-3):276–308. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

