Optimized Ribociclib nanostructured lipid carrier for the amelioration of skin cancer: Inferences from ex-vivo skin permeation and dermatokinetic studies
- PMID: 38384476
- PMCID: PMC10879011
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2024.101984
Optimized Ribociclib nanostructured lipid carrier for the amelioration of skin cancer: Inferences from ex-vivo skin permeation and dermatokinetic studies
Abstract
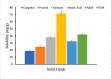
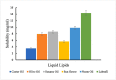
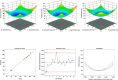
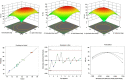
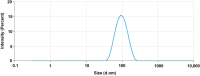
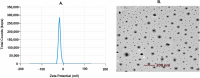
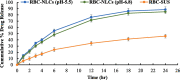
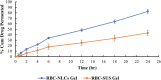
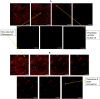
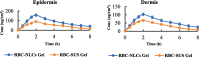
Current research focuses on explicitly developing and evaluating nanostructured lipidic carriers (NLCs) for the chemotherapeutic drug Ribociclib (RCB) via the topical route to surmount the inherent bioavailability shortcomings. The absolute oral bioavailability has not been determined, but using a physiologically based pharmacokinetic model it was predicted that 65.8 % of the standard dose of RCB (600 mg) would be absorbed mainly in the small intestine. RCB-NLCs were produced using the solvent evaporation method, and Box-Behnken Design (BBD) was employed to optimize composition. The prepared NLCs had an average PS of 79.29 ± 3.53 nm, PDI of 0.242 ± 0.021, and a %EE of 86.07 ± 3.14. The TEM analysis disclosed the spherical form and non-aggregative nature of the NLCs. The outcomes of an in-vitro release investigation presented cumulative drug release of 84.97 ± 3.37 % in 24 h, significantly higher than that from the RCB suspension (RCB-SUS). Ex-vivo skin permeation investigations on rodent (Swiss albino mice) revealed that RCB-NLCs have 1.91 times increases in skin permeability comparable to RCB-SUS. Compared to RCB-SUS, RCB-NLCs were able to penetrate deeper into the epidermis membrane than RCB-SUS as per the findings of confocal microscopy. In dermatokinetic study, higher amount of RCB was maintained in both the layers of mice's skin when treated with RCB-NLCs gel comparable to the RCB-SUS gel preparation. The in-vitro, ex-vivo, CLSM, and dermatokinetics data demonstrated a significant possibility for this novel RCB formulation to be effective against skin cancer.
Keywords: BoxBehnken Design; CLSM; Dermatokinetics; Nanostructured Lipidic Carriers; Ribociclib; Skin cancer.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmed M.M., Fatima F., Alali A., Kalam M.A., Alhazzani K., Bhatia S., Alshehri S., Ghoneim M.M. Ribociclib-loaded ethylcellulose-based nanosponges: formulation, physicochemical characterization, and cytotoxic potential against breast cancer. Adsorp. Sci. Tech. 2022 doi: 10.1155/2022/1922263. - DOI
-
- Alam T., Khan S., Gaba B., Haider M.F., Baboota S., Ali J. Adaptation of quality by design-based development of isradipine nanostructured-lipid carrier and its evaluation for in vitro gut permeation and in vivo solubilization fate. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018;107:2914–2926. doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2018.07.021. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alhalmi A., Amin S., Khan Z., Beg S., Al Kamaly O., Saleh A., Kohli K. Nanostructured lipid carrier-based codelivery of raloxifene and naringin: formulation, optimization, in vitro, ex vivo, in vivo assessment, and acute toxicity studies. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14:1771. doi: 10.3390/PHARMACEUTICS14091771/S1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

