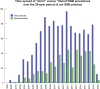
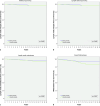
Strict versus Liberal Use of Sentinel Node Biopsy in Breast Cancer Surgery: Any Clinical Outcome Differences? A 20-Year Clinical Experience
- PMID: 38384490
- PMCID: PMC10878707
- DOI: 10.1159/000533731
Strict versus Liberal Use of Sentinel Node Biopsy in Breast Cancer Surgery: Any Clinical Outcome Differences? A 20-Year Clinical Experience
Abstract
Introduction: As applied to early breast cancer (BC) patients, sentinel node biopsy (SNB) has undergone major changes over the years, especially concerning the widening of indication criteria or skipping systematic axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) after a positive SN. We aimed to ascertain whether a strict versus a more liberal use of SNB resulted in different clinical outcomes in our clinical experience.
Methods: We studied consecutive BC patients undergoing SNB between January 1, 2000, and March 31, 2020. There were 1,587 patients and 1,634 SNB procedures. Cases were divided into two study groups: the "strict" SNB group (unifocal tumors up to 35 mm in which ALND was always performed for a positive SN, amounting to 1,183 SNBs), and the "liberal" SNB group (extended tumor size up to selected T3 cases, as well as multifocal or bilateral disease, and patients with previous contralateral BC, not always followed by ALND after a positive SN, amounting to 451 SNBs). Patients were closely followed up to the end of the study.
Results: Clinico-pathological variables were strikingly different between study groups, with the liberal group showing a higher risk profile. Cox regression analysis for disease recurrence did not show significant differences in axillary, lymph node, or locoregional recurrence rates or distant relapse. There were no differences in survival between groups.
Conclusion: It seems reasonable to adopt the liberal SNB approach, as the goal of surgical management in early BC patients must be attaining optimal locoregional disease control, no matter the differences in distant metastatic spread rates across different BC risk profiles.
Keywords: Axillary recurrence; Breast cancer; Sentinel node biopsy; Survival.
© 2023 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sentinel node biopsy in early breast cancer: lessons learned from more than 1000 cases at a single institution.Tumori. 2012 Jul-Aug;98(4):413-20. doi: 10.1177/030089161209800403. Tumori. 2012. PMID: 23052155
-
Repeat sentinel node biopsy should be considered in patients with locally recurrent breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015 Oct;153(3):549-56. doi: 10.1007/s10549-015-3571-4. Epub 2015 Sep 10. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015. PMID: 26358709
-
Patterns in the Use of Axillary Operations for Patients with Node-Positive Breast Cancer After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: A National Cancer Database (NCDB) Analysis.Ann Surg Oncol. 2019 Oct;26(10):3305-3311. doi: 10.1245/s10434-019-07540-3. Epub 2019 Jul 24. Ann Surg Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31342364
-
Omission of sentinel node biopsy for breast cancer: Historical context and future perspectives on a modern controversy.Cancer. 2021 Dec 1;127(23):4376-4383. doi: 10.1002/cncr.33960. Epub 2021 Oct 6. Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34614216 Review.
-
[Prognostic and curative value of sentinel node in breast cancer. A 377 patients experience].Ann Ital Chir. 2010 Mar-Apr;81(2):103-11; discussion 112-3. Ann Ital Chir. 2010. PMID: 20726388 Review. Italian.
References
-
- Veronesi U, Paganelli G, Galimberti V, Viale G, Zurrida S, Bedoni M. Sentinel-node biopsy to avoid axillary dissection in breast cancer with clinically negative lymph-nodes. Lancet. 1997 Jun 28;349(9069):1864–7. - PubMed
-
- Donker M, Straver ME, van Tienhoven G, van de Velde CJH, Mansel RE, Litière S, et al. . Comparison of the sentinel node procedure between patients with multifocal and unifocal breast cancer in the EORTC 10981-22023 AMAROS Trial: identification rate and nodal outcome. Eur J Cancer. 2013 jun;49(9):2093–100. 10.1016/j.ejca.2013.02.017. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials