Combination therapy with Hordeum vulgare, Elettaria cardamomum, and Cicer arietinum exhibited anti-diabetic potential through modulation of oxidative stress and proinflammatory cytokines
- PMID: 38384558
- PMCID: PMC10879019
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26126
Combination therapy with Hordeum vulgare, Elettaria cardamomum, and Cicer arietinum exhibited anti-diabetic potential through modulation of oxidative stress and proinflammatory cytokines
Retraction in
-
Retraction notice to "Combination therapy with Hordeum vulgare, Elettaria cardamomum, and Cicer arietinum exhibited anti-diabetic potential through modulation of oxidative stress and proinflammatory cytokines" [Heliyon 10 (2024) e26126].Heliyon. 2025 Mar 12;11(6):e43154. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e43154. eCollection 2025 Mar 20. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 40201512 Free PMC article.
Abstract
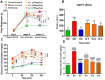
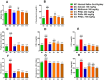
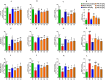
Poly-herbal therapies for chronic diseases like diabetes mellitus (DM) have been practiced in south Asia for centuries. One of such therapies comprises of Hordeum vulgare, Elettaria cardamomum and Cicer arietinum that have shown encouraging therapeutic potential in the treatment of diabetes and obesity. Therefore, poly-herbal granules (PHGs) of this formula were developed and investigated for their anti-diabetic and anti-obesity potential in obese-diabetic rats. The developed PHGs were chemical characterized and the virtual molecular docking was performed by Discovery studio visualizer (DSV) software. For in-vivo experiment, obesity in rats was induced with high-fat high-sugar diet. After that, diabetes was induced by alloxan monohydrate 150 mg/kg i.p. injection. The diseased rats were treated with PHGs at 250, 500 and 750 mg/kg/day for four weeks. GC-MS analysis of PHGs demonstrated the presence of 1,3-Benzenedicarboxylic acid bis(2-ethylhexyl) ester and 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid di-isooctyl ester and phenol, 2,4-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl). Molecular docking of these compounds demonstrated higher binding energies with receptor than metformin against α-amylase and α-glucosidase. PHGs exhibited a decline in body weight, HbA1c, hyperlipidemia, hyperglycemia, and insulin resistance in diseased rats. The histopathological examination revealed that PHGs improved the alloxan-induced damage to the pancreas. Furthermore, PHGs increased the SOD, CAT and GSH while and the decreased the level of MDA in the liver, kidney and pancreas of diseased rats. Additionally, the PHGs had significantly downregulated the TNF-α and NF-κB while upregulated the expression of NrF-2. The current study demonstrated that the PHGs exhibited anti-diabetic and anti-obesity potential through amelioration of oxidative stress, NF-κB, TNF-α, and NrF-2 due to the presence of different phytochemicals.
Keywords: Diabetes; Inflammation; Obesity; Oxidative stress; Poly-herbal therapy.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Lovic D., Piperidou A., Zografou I., Grassos H., Pittaras A., Manolis A. The growing epidemic of diabetes mellitus. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2020;18(2):104–109. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

