A Triad of Shoulder Injuries Following Cardioversion: A Case Report
- PMID: 38384611
- PMCID: PMC10879726
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.52704
A Triad of Shoulder Injuries Following Cardioversion: A Case Report
Abstract
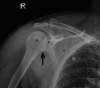
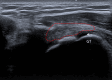
Transthoracic defibrillation and cardioversion are commonly used techniques to resuscitate a patient during acute cardiac arrhythmic events. There are numerous complications associated with these procedures. We report a previously unreported complication where a patient suffered from a supraspinatus tear after cardioversion for ventricular tachycardia. There are numerous complications associated with these procedures. We report a previously unreported complication where a middle-aged Chinese patient with no previous trauma history suffered from a supraspinatus tear after cardioversion for ventricular tachycardia.
Keywords: bankart lesion; cardioversion; case report; shoulder dislocation; supraspinatus tear.
Copyright © 2024, Tan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anterior capsulolabral lesions combined with supraspinatus tendon tears: biomechanical effects of the pathologic condition and repair in human cadaveric shoulders.Arthroscopy. 2013 Sep;29(9):1492-7. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2013.05.031. Epub 2013 Jul 30. Arthroscopy. 2013. PMID: 23910002
-
Efficacy of automatic multimodal device therapy for ventricular tachyarrhythmias as delivered by a new implantable pacing cardioverter-defibrillator. Results of a European multicenter study of 102 implants.Circulation. 1992 Aug;86(2):363-74. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.86.2.363. Circulation. 1992. PMID: 1638705 Clinical Trial.
-
[Low energy cardioversion with the implantable cardioversion defibrillator devices for treatment of ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation].Z Kardiol. 1993 Nov;82(11):683-91. Z Kardiol. 1993. PMID: 8291289 German.
-
[Electrical defibrillation and cardioversion].Medicina (Kaunas). 2005;41(10):892-9. Medicina (Kaunas). 2005. PMID: 16272838 Review. Lithuanian.
-
[Shoulder instability and rotator cuff tear].Orthopade. 2009 Jan;38(1):70-4. doi: 10.1007/s00132-008-1356-8. Orthopade. 2009. PMID: 19139844 Review. German.
References
-
- Ventricular tachycardia rate and morphology determine energy and current requirements for transthoracic cardioversion. Kerber RE, Kienzle MG, Olshansky B, et al. Circulation. 1992;85:158–163. - PubMed
-
- Primary anterior shoulder dislocation and rotator cuff tears. Berbig R, Weishaupt D, Prim J, Shahin O. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1999;8:220–225. - PubMed
-
- Correlation between Bankart and Hill-Sachs lesions in anterior shoulder dislocation. Widjaja AB, Tran A, Bailey M, Proper S. ANZ J Surg. 2006;76:436–438. - PubMed
-
- Randomized trial comparing the effectiveness of internal (through implantable cardioverter defibrillator) versus external cardioversion of atrial fibrillation. Elayi CS, Parrott K, Etaee F, et al. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2020;58:261–267. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
