Leveraging the transcriptome to further our understanding of GWAS findings: eQTLs associated with genes related to LDL and LDL subclasses, in a cohort of African Americans
- PMID: 38384714
- PMCID: PMC10879560
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1345541
Leveraging the transcriptome to further our understanding of GWAS findings: eQTLs associated with genes related to LDL and LDL subclasses, in a cohort of African Americans
Abstract
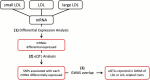
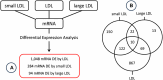
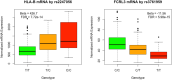
Background: GWAS discoveries often pose a significant challenge in terms of understanding their underlying mechanisms. Further research, such as an integration with expression quantitative trait locus (eQTL) analyses, are required to decipher the mechanisms connecting GWAS variants to phenotypes. An eQTL analysis was conducted on genes associated with low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and its subclasses, with the aim of pinpointing genetic variants previously implicated in GWAS studies focused on lipid-related traits. Notably, the study cohort consisted of African Americans, a population characterized by a heightened prevalence of hypercholesterolemia. Methods: A comprehensive differential expression (DE) analysis was undertaken, with a dataset of 17,948 protein-coding mRNA transcripts extracted from the whole-blood transcriptomes of 416 samples to identify mRNA transcripts associated with LDL, with further granularity delineated between small LDL and large LDL subclasses. Subsequently, eQTL analysis was conducted with a subset of 242 samples for which whole-genome sequencing data were available to identify single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with the LDL-related mRNA transcripts. Lastly, plausible functional connections were established between the identified eQTLs and genetic variants reported in the GWAS catalogue. Results: DE analysis revealed 1,048, 284, and 94 mRNA transcripts that exhibited differential expression in response to LDL, small LDL, and large LDL, respectively. The eQTL analysis identified a total of 9,950 significant SNP-mRNA associations involving 6,955 SNPs including a subset 101 SNPs previously documented in GWAS of LDL and LDL-related traits. Conclusion: Through comprehensive differential expression analysis, we identified numerous mRNA transcripts responsive to LDL, small LDL, and large LDL. Subsequent eQTL analysis revealed a rich landscape of eQTL-mRNA associations, including a subset of eQTL reported in GWAS studies of LDL and related traits. The study serves as a testament to the important role of integrative genomics in unraveling the enigmatic GWAS relationships between genetic variants and the complex fabric of human traits and diseases.
Keywords: African American (AA); GWAS; LDL; eQTL; transcriptome.
Copyright © 2024 Abbas, Diallo, Goodney and Gaye.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endometrial vezatin and its association with endometriosis risk.Hum Reprod. 2016 May;31(5):999-1013. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dew047. Epub 2016 Mar 22. Hum Reprod. 2016. PMID: 27005890
-
Missing Regulation Between Genetic Association and Transcriptional Abundance for Hypercholesterolemia Genes.Genes (Basel). 2025 Jan 15;16(1):84. doi: 10.3390/genes16010084. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39858631 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic study of taste perception genes in African Americans reveals SNPs linked to Alzheimer's disease.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 16;14(1):21560. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71669-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39284855 Free PMC article.
-
Expression Quantitative Trait Loci Information Improves Predictive Modeling of Disease Relevance of Non-Coding Genetic Variation.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 16;10(10):e0140758. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140758. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26474488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From GWAS to Gene: Transcriptome-Wide Association Studies and Other Methods to Functionally Understand GWAS Discoveries.Front Genet. 2021 Sep 30;12:713230. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.713230. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34659337 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Broad Institute. (2015). broadinstitute/gtex-pipeline: GTEx v8, 2018.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

