Oral_voting_transfer: classification of oral microorganisms' function proteins with voting transfer model
- PMID: 38384719
- PMCID: PMC10879614
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1277121
Oral_voting_transfer: classification of oral microorganisms' function proteins with voting transfer model
Abstract
Introduction: The oral microbial group typically represents the human body's highly complex microbial group ecosystem. Oral microorganisms take part in human diseases, including Oral cavity inflammation, mucosal disease, periodontal disease, tooth decay, and oral cancer. On the other hand, oral microbes can also cause endocrine disorders, digestive function, and nerve function disorders, such as diabetes, digestive system diseases, and Alzheimer's disease. It was noted that the proteins of oral microbes play significant roles in these serious diseases. Having a good knowledge of oral microbes can be helpful in analyzing the procession of related diseases. Moreover, the high-dimensional features and imbalanced data lead to the complexity of oral microbial issues, which can hardly be solved with traditional experimental methods.
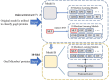
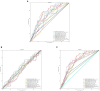
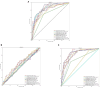
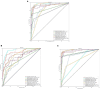
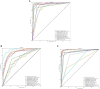
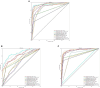
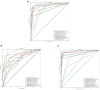
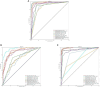
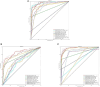
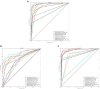
Methods: To deal with these challenges, we proposed a novel method, which is oral_voting_transfer, to deal with such classification issues in the field of oral microorganisms. Such a method employed three features to classify the five oral microorganisms, including Streptococcus mutans, Staphylococcus aureus, abiotrophy adjacent, bifidobacterial, and Capnocytophaga. Firstly, we utilized the highly effective model, which successfully classifies the organelle's proteins and transfers to deal with the oral microorganisms. And then, some classification methods can be treated as the local classifiers in this work. Finally, the results are voting from the transfer classifiers and the voting ones.
Results and discussion: The proposed method achieved the well performances in the five oral microorganisms. The oral_voting_transfer is a standalone tool, and all its source codes are publicly available at https://github.com/baowz12345/voting_transfer.
Keywords: bioinformatics; classification; machine learning; oral microorganisms proteins; voting transfer model.
Copyright © 2024 Bao, Liu and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Arlot S., Genuer R. (2016). Comments on: A random forest guided tour. Test 25, 228–238. 10.1007/s11749-016-0484-4 - DOI
-
- Awais M., Hussain W., Khan Y., Rasool N., Khan S., Chou K. (2019). iPhosH-PseAAC: identify phosphohistidine sites in proteins by blending statistical moments and position relative features according to the Chou’s 5-step rule and general pseudo amino acid composition. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 18 596–610. 10.1109/TCBB.2019.2919025 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

