Enhancing growth, vitality, and aromatic richness: unveiling the dual magic of silicon dioxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles in Ocimum tenuiflorum L
- PMID: 38384769
- PMCID: PMC10880381
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1335965
Enhancing growth, vitality, and aromatic richness: unveiling the dual magic of silicon dioxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles in Ocimum tenuiflorum L
Abstract
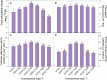
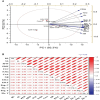
Ocimum tenuiflorum, commonly known as "Holy basil," is renowned for its notable medicinal and aromatic attributes. Its unique fragrance attributes to specific volatile phytochemicals, primarily belonging to terpenoid and/or phenylpropanoid classes, found within their essential oils. The use of nanoparticles (NPs) in agriculture has attracted attention among plant researchers. However, the impact of NPs on the modulation of morpho-physiological aspects and essential oil production in medicinal plants has received limited attention. Consequently, the present study aimed to explore the effect of silicon dioxide (SiO2) and titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles at various concentrations (viz., DDW (control), Si50+Ti50, Si100+Ti50, Si100+Ti100, Si200+Ti100, Si100+Ti200 and Si200+Ti200 mg L-1) on growth, physiology and essential oil production of O. tenuiflorum at 120 days after planting (DAP). The results demonstrated that the combined application of Si and Ti (Si100+Ti100 mg L-1) exhibited the most favourable outcomes compared to the other combinational treatments. This optimal treatment significantly increased the vegetative growth parameters (root length (33.5%), shoot length (39.2%), fresh weight (62.7%) and dry weight (28.5%)), photosynthetic parameters, enzymatic activities (nitrate reductase and carbonic anhydrase), the overall area of PGTs (peltate glandular trichomes) and essential oil content (172.4%) and yield (323.1%), compared to the control plants. Furthermore, the GCMS analysis showed optimal treatment (Si100+Ti100) significantly improved the content (43.3%) and yield (151.3%) of eugenol, the primary active component of the essential oil. This study uncovers a remarkable and optimal combination of SiO2 and TiO2 nanoparticles that effectively enhances the growth, physiology, and essential oil production in Holy basil. These findings offer valuable insights into maximizing the potential benefits of its use in industrial applications.
Keywords: essential oil; eugenol; holy basil; nanoparticles; nitrate reductase.
Copyright © 2024 Bhat, Uddin, Chishti, Singh, Singh, Khan and Mukarram.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Combined application of SiO2 and TiO2 nanoparticles enhances growth characters, physiological attributes and essential oil production of Coleus aromatics Benth.Heliyon. 2023 Nov 9;9(11):e21646. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21646. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38058652 Free PMC article.
-
Interspecies comparative features of trichomes in Ocimum reveal insights for biosynthesis of specialized essential oil metabolites.Protoplasma. 2019 Jul;256(4):893-907. doi: 10.1007/s00709-018-01338-y. Epub 2019 Jan 18. Protoplasma. 2019. PMID: 30656458
-
Enhancing growth, yield, essential oil content, and composition of holy basil (Ocimum tenuiflorum L.) using red algae-based bio-stimulant under acidic conditions of the Western Himalayas.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Jan 22;25(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06064-1. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 39838299 Free PMC article.
-
Ocimum sanctum L (Holy Basil or Tulsi) and its phytochemicals in the prevention and treatment of cancer.Nutr Cancer. 2013;65 Suppl 1:26-35. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2013.785010. Nutr Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23682780 Review.
-
A glance at the chemodiversity of Ocimum species: Trends, implications, and strategies for the quality and yield improvement of essential oil.Phytochem Rev. 2022;21(3):879-913. doi: 10.1007/s11101-021-09767-z. Epub 2021 Aug 2. Phytochem Rev. 2022. PMID: 34366748 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Green nanoscience for healthcare: Advancing biomedical innovation through eco-synthesized nanoparticle.Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2025 Aug 12;47:e00913. doi: 10.1016/j.btre.2025.e00913. eCollection 2025 Sep. Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2025. PMID: 40895589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synergistic Effect of TiO2-Nanoparticles and Plant Growth-Promoting Microorganisms on the Physiological Parameters and Antioxidant Responses of Capsicum annum Cultivars.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Jun 10;14(6):707. doi: 10.3390/antiox14060707. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40563339 Free PMC article.
-
Unlocking the potential of titanium dioxide nanoparticles: an insight into green synthesis, optimizations, characterizations, and multifunctional applications.Microb Cell Fact. 2024 Dec 23;23(1):341. doi: 10.1186/s12934-024-02609-5. Microb Cell Fact. 2024. PMID: 39710687 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams R. P. (2007). Identification of essential oil components by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry Vol. 456 (Carol Stream: Allured Publishing Corporation; ), 544–545.
-
- Ahmad B., Khan M., Jaleel H., Shabbir A., Sadiq Y., Uddin M. (2020). Silicon nanoparticles mediated increase in glandular trichomes and regulation of photosynthetic and quality attributes in Mentha piperita L. J. Plant Growth Regul. 39 (1), 346–357. doi: 10.1007/s00344-019-09986-x - DOI
-
- Ahmad B., Shabbir A., Jaleel H., Masroor M., Khan A., Sadiq Y. (2018). Efficacy of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in modulating photosynthesis, peltate glandular trichomes and essential oil production and quality in Mentha piperita L. Curr. Plant Biol. 13, 6–15. doi: 10.1016/j.cpb.2018.04.002 - DOI
-
- Ahmed K. B. M., Khan M., Shabbir A., Ahmad B., Uddin M., Azam A. (2022). Comparative effect of foliar application of silicon, titanium and zinc nanoparticles on the performance of vetiver-a medicinal and aromatic plant. Silicon. 15, 153–166. doi: 10.1007/s12633-022-02007-9 - DOI
-
- Ali M., Anjum N., Ain Q. T., He J. H. (2021). Homotopy perturbation method for the attachment oscillator arising in nanotechnology. Fibers Polymers 22, 1601–1606. doi: 10.1007/s12221-021-0844-x - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

