An ascomycete H4 variant with an unknown function
- PMID: 38384781
- PMCID: PMC10878826
- DOI: 10.1098/rsos.231705
An ascomycete H4 variant with an unknown function
Abstract
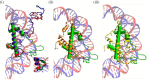
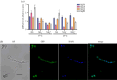
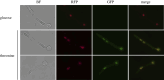
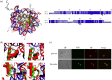
Histone variants leading to altered nucleosome structure, dynamics and DNA accessibility occur frequently, albeit rarely for H4. We carried out a comprehensive in silico scrutiny of fungal genomes, which revealed the presence of a novel H4 variant (H4E) in the ascomycetes, throughout the Pezizomycotina, in basal species of the Taphrinomycotina and also in the Glomeromycota. The coding cognate genes show a specific intron/exon organization, different from H4 canonical genes. H4Es diverge from canonical H4s mainly in the N- and C-terminal extensions, showing marked differences in the distribution and number of Lys and Arg residues, which may result in novel post-translational modifications. In Aspergillus nidulans (Pezizomycotina, Eurotiomycetes) the H4E variant protein level is low in mycelia. However, the encoding gene is well expressed at 37°C under nitrogen starvation. H4E localizes to the nucleus and interacts with H3, but its absence or overexpression does not result in any detectable phenotype. Deletion of only one of the of the two canonical H4 genes results in a strikingly impaired growth phenotype, which indicates that H4E cannot replace this canonical histone. Thus, an H4 variant is present throughout a whole subphylum of the ascomycetes, but with hitherto no experimentally detectable function.
Keywords: ascomycetes; chromatin; histone H4 variant.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Evidence indicating proximity in the nucleosome between the histone H4 N termini and the globular domain of histone H1.J Mol Biol. 1994 Oct 14;243(1):48-59. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1629. J Mol Biol. 1994. PMID: 7932740
-
Histone H4-lysine 20 monomethylation is increased in promoter and coding regions of active genes and correlates with hyperacetylation.J Biol Chem. 2005 Nov 18;280(46):38814-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M505563200. Epub 2005 Sep 15. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16166085
-
Comprehensive structural analysis of mutant nucleosomes containing lysine to glutamine (KQ) substitutions in the H3 and H4 histone-fold domains.Biochemistry. 2011 Sep 13;50(36):7822-32. doi: 10.1021/bi201021h. Epub 2011 Aug 17. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21812398
-
H3-H4 Histone Chaperone Pathways.Annu Rev Genet. 2018 Nov 23;52:109-130. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-120417-031547. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Annu Rev Genet. 2018. PMID: 30183406 Review.
-
Post-Translational Modifications of H2A Histone Variants and Their Role in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Feb 27;10(3):59. doi: 10.3390/cancers10030059. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29495465 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

