CT-based radiomics for predicting Ki-67 expression in lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38384802
- PMCID: PMC10879429
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1329801
CT-based radiomics for predicting Ki-67 expression in lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Radiomics, an emerging field, presents a promising avenue for the accurate prediction of biomarkers in different solid cancers. Lung cancer remains a significant global health challenge, contributing substantially to cancer-related mortality. Accurate assessment of Ki-67, a marker reflecting cellular proliferation, is crucial for evaluating tumor aggressiveness and treatment responsiveness, particularly in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
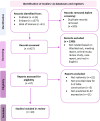
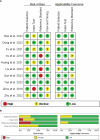
Methods: A systematic review and meta-analysis conducted following the preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy studies (PRISMA-DTA) guidelines. Two authors independently conducted a literature search until September 23, 2023, in PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science. The focus was on identifying radiomics studies that predict Ki-67 expression in lung cancer. We evaluated quality using both Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies (QUADAS-2) and the Radiomics Quality Score (RQS) tools. For statistical analysis in the meta-analysis, we used STATA 14.2 to assess sensitivity, specificity, heterogeneity, and diagnostic values.
Results: Ten retrospective studies were pooled in the meta-analysis. The findings demonstrated that the use of computed tomography (CT) scan-based radiomics for predicting Ki-67 expression in lung cancer exhibited encouraging diagnostic performance. Pooled sensitivity, specificity, and area under the curve (AUC) in training cohorts were 0.78, 0.81, and 0.85, respectively. In validation cohorts, these values were 0.78, 0.70, and 0.81. Quality assessment using QUADAS-2 and RQS indicated generally acceptable study quality. Heterogeneity in training cohorts, attributed to factors like contrast-enhanced CT scans and specific Ki-67 thresholds, was observed. Notably, publication bias was detected in the training cohort, indicating that positive results are more likely to be published than non-significant or negative results. Thus, journals are encouraged to publish negative results as well.
Conclusion: In summary, CT-based radiomics exhibit promise in predicting Ki-67 expression in lung cancer. While the results suggest potential clinical utility, additional research efforts should concentrate on enhancing diagnostic accuracy. This could pave the way for the integration of radiomics methods as a less invasive alternative to current procedures like biopsy and surgery in the assessment of Ki-67 expression.
Keywords: CT-scan; Ki-67; artificial intelligence; lung cancer; machine learning; radiomics.
Copyright © 2024 Luo, Zheng, Zhang, He, Luo, Jiang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Radiomics diagnostic performance for predicting lymph node metastasis in esophageal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Med Imaging. 2024 Jun 12;24(1):144. doi: 10.1186/s12880-024-01278-5. BMC Med Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38867143 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic performance of CT scan-based radiomics for prediction of lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2023 Oct 23;13:1185663. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1185663. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37936604 Free PMC article.
-
A Bayesian meta-analysis on MRI-based radiomics for predicting EGFR mutation in brain metastasis of lung cancer.BMC Med Imaging. 2025 Feb 10;25(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s12880-025-01566-8. BMC Med Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39930347 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of 18F-FDG PET/CT radiomics for EGFR mutation status in non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2024 Feb 1;14:1281572. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1281572. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38361781 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of CT scan-based radiomics in intracerebral hemorrhage patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Radiol. 2024 Sep;178:111652. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2024.111652. Epub 2024 Jul 26. Eur J Radiol. 2024. PMID: 39079323
Cited by
-
Preoperative CT radiomics-based model for predicting Ki-67 expression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Nov 28;49(11):1722-1731. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2024.240455. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 40177755 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Manual Delineation of the Region of Interest Combined With Clinical Image Analysis to Predict the Ki-67 Expression Level in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer.Sage Open Pathol. 2025 May 12;18:30502098251336608. doi: 10.1177/30502098251336608. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Sage Open Pathol. 2025. PMID: 40519328 Free PMC article.
-
The value of morphological magnetic resonance imaging features combined with diffusion kurtosis imaging for predicting Ki-67 expression levels in high-grade gliomas.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025 Apr 1;15(4):2813-2826. doi: 10.21037/qims-24-2035. Epub 2025 Mar 21. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025. PMID: 40235755 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of Ki-67 Expression in HIV-Associated Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients Using Multiple Machine Learning Models Based on CT Imaging Radiomics.Cancer Manag Res. 2025 Apr 25;17:881-892. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S505390. eCollection 2025. Cancer Manag Res. 2025. PMID: 40303969 Free PMC article.
-
MRI radiomics-based interpretable model and nomogram for preoperative prediction of Ki-67 expression status in primary central nervous system lymphoma.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Jun 27;11:1345162. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1345162. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38994341 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

