UPP1 enhances bladder cancer progression and gemcitabine resistance through AKT
- PMID: 38385072
- PMCID: PMC10878145
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.83774
UPP1 enhances bladder cancer progression and gemcitabine resistance through AKT
Abstract
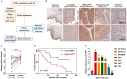
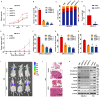
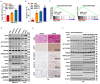
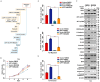
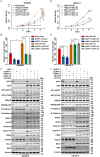
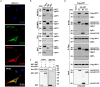
UPP1, a crucial pyrimidine metabolism-related enzyme, catalyzes the reversible phosphorylation of uridine to uracil and ribose-1-phosphate. However, the effects of UPP1 in bladder cancer (BLCA) have not been elucidated. AKT, which is activated mainly through dual phosphorylation (Thr308 and Ser473), promotes tumorigenesis by phosphorylating downstream substrates. This study demonstrated that UPP1 promotes BLCA cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and gemcitabine resistance by activating the AKT signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo. Additionally, UPP1 promoted AKT activation by facilitating the binding of AKT to PDK1 and PDK2 and the recruitment of phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosphate to AKT. Moreover, the beneficial effects of UPP1 on BLCA tumorigenesis were mitigated upon UPP1 mutation with Arg94 or MK2206 treatment (AKT-specific inhibitor). AKT overexpression or SC79 (AKT-specific activator) treatment restored tumor malignancy and drug resistance. Thus, this study revealed that UPP1 is a crucial oncogene and a potential therapeutic target for BLCA and that UPP1 activates the AKT signaling pathway and enhances tumorigenesis and drug resistance to gemcitabine.
Keywords: AKT; UPP1; bladder cancer.; gemcitabine; metastasis.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


References
-
- Jubber I, Ong S, Bukavina L, Black PC, Compérat E, Kamat AM. et al. Epidemiology of Bladder Cancer in 2023: A Systematic Review of Risk Factors. Eur Urol. 2023;84:176–90. - PubMed
-
- Lenis AT, Lec PM, Chamie K, Mshs MD. Bladder Cancer: A Review. JAMA. 2020;324:1980–91. - PubMed
-
- Patel VG, Oh WK, Galsky MD. Treatment of muscle-invasive and advanced bladder cancer in 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:404–23. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

