Efficient conversion of aromatic and phenylpropanoid alcohols to acids by the cascade biocatalysis of alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenases
- PMID: 38385148
- PMCID: PMC10876487
- DOI: 10.1016/j.synbio.2024.01.008
Efficient conversion of aromatic and phenylpropanoid alcohols to acids by the cascade biocatalysis of alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenases
Abstract
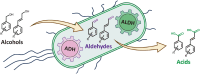
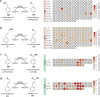
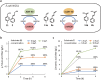
Benzyl and phenylpropanoid acids are widely used in organic synthesis of fine chemicals, such as pharmaceuticals and condiments. However, biocatalysis of these acids has received less attention than chemical synthesis. One of the main challenges for biological production is the limited availability of alcohol dehydrogenases and aldehyde dehydrogenases. Environmental microorganisms are potential sources of these enzymes. In this study, 129 alcohol dehydrogenases and 42 aldehyde dehydrogenases from Corynebacterium glutamicum, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Bacillus subtilis were identified and explored with various benzyl and phenylpropanoid alcohol and aldehyde substrates, among which four alcohol dehydrogenases and four aldehyde dehydrogenases with broad substrate specificity and high catalytic activity were obtained. Moreover, a cascade whole-cell catalytic system including ADH-90, ALDH-40, and the NAD(P)H oxidase LreNox was established, which showed high efficiency in converting cinnamyl alcohol and p-methylbenzyl alcohol into the respective carboxylic acids. Remarkably, this biocatalytic system can be easily scaled up to gram-level production, facilitating preparation purposes.
Keywords: Alcohol dehydrogenases; Aldehyde dehydrogenases; Benzyl acids; Phenylpropanoid acids; Whole-cell catalysis.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

