IELSG38: phase II trial of front-line chlorambucil plus subcutaneous rituximab induction and maintenance in mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma
- PMID: 38385243
- PMCID: PMC11290511
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2023.283918
IELSG38: phase II trial of front-line chlorambucil plus subcutaneous rituximab induction and maintenance in mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma
Abstract
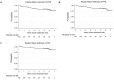
The IELSG38 trial was conducted to investigate the effects of subcutaneous (SC) rituximab on the complete remission (CR) rate and the benefits of SC rituximab maintenance in patients with extranodal marginal zone lymphoma (MZL) who received front-line treatment with chlorambucil plus rituximab. Study treatment was an induction phase with oral chlorambucil 6 mg/m2/day on weeks 1-6, 9-10, 13-14, 17-18, and 21-22, and intravenous rituximab 375 mg/m2 on day 1 of weeks 1-4, and 1,400 mg SC on weeks 9, 13, 17, and 21. Then, a maintenance phase followed with rituximab administered at 1,400 mg SC every two months for two years. Of the 112 patients enrolled, 109 were evaluated for efficacy. The CR rates increased from 52% at the end of the induction phase to 70% upon completion of the maintenance phase. With a median follow-up of 5.8 years, the 5-year event-free, progression-free, and overall survival rates were 87% (95% CI: 78-92), 84% (95% CI: 75-89), and 93% (95% CI: 86-96), respectively. The most common grade ≥3 toxicities were neutropenia (33%) and lymphocytopenia (16%). Six patients experienced treatment-related serious adverse events, including fever of unknown origin, sepsis, pneumonia, respiratory failure, severe cerebellar ataxia, and fatal acute myeloid leukemia. The trial showed that SC rituximab did not improve the CR rate at the conclusion of the induction phase, which was the main endpoint. Nevertheless, SC rituximab maintenance might have facilitated long-term disease control, potentially contributing to enhanced event-free and progression-free survival.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01808599.
Figures

Comment in
-
More is not always better, sometimes it is just more.Haematologica. 2024 Aug 1;109(8):2395-2397. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2024.285019. Haematologica. 2024. PMID: 38546661 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

