In-Office Needle Arthroscopy: Indications, Surgical Techniques, Tips, and Tricks
- PMID: 38385718
- PMCID: PMC10883628
- DOI: 10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-23-00124
In-Office Needle Arthroscopy: Indications, Surgical Techniques, Tips, and Tricks
Abstract
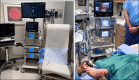
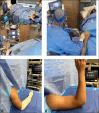
In-office needle arthroscopy (IONA) has gained increased attention as a minimally invasive alternative to standard arthroscopy performed in the operating room (OR) setting. IONA uses instrumentation that is markedly smaller in size and diameter making arthroscopy less invasive. Less OR equipment and less OR staff are required resulting in procedures that may be more accessible and less expensive. IONA is typically performed using local intra-articular blocks, thereby reducing the need for regional anesthesia or general anesthesia along with its associated risks. Using a clinic setting rather than an OR reduces the cost and increases the efficiency of the procedure. This article will present the indications for IONA in upper and lower extremity injuries and will describe the best practice office setup. Technical pearls and pitfalls will also be discussed.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In-Office Needle Arthroscopy: A Systematic Review of Indications and Clinical Utility.Arthroscopy. 2019 Sep;35(9):2709-2721. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2019.03.045. Epub 2019 Aug 12. Arthroscopy. 2019. PMID: 31416656
-
In-office needle arthroscopy is a cost-effective alternative for operating room diversion in medial meniscectomy: a financial analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2023 Jun 15;18(1):435. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-03866-7. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 37322494 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial Commentary: What You See Is What You Get-Is In-Office Needle Arthroscopy Ready for Prime Time?Arthroscopy. 2019 Sep;35(9):2722-2723. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2019.06.032. Arthroscopy. 2019. PMID: 31500760
-
In-Office Needle Arthroscopy with Meniscal Repair for Meniscal Lesions of the Knee.Arthrosc Tech. 2023 Sep 25;12(10):e1821-e1826. doi: 10.1016/j.eats.2023.06.013. eCollection 2023 Oct. Arthrosc Tech. 2023. PMID: 37942106 Free PMC article.
-
Regional anesthesia outside the operating room: indications and techniques.Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2012 Aug;25(4):501-7. doi: 10.1097/ACO.0b013e3283556f58. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2012. PMID: 22673788 Review.
Cited by
-
Percutaneous Biceps Tenodesis Using Needle Arthroscopy and Regional Anesthesia: The Infinity Technique.Arthrosc Tech. 2025 Jan 29;14(5):103414. doi: 10.1016/j.eats.2024.103414. eCollection 2025 May. Arthrosc Tech. 2025. PMID: 40548016 Free PMC article.
-
Nano-Arthroscopic Plantar Fascia Release Technique.Arthrosc Tech. 2024 Jul 25;13(11):103118. doi: 10.1016/j.eats.2024.103118. eCollection 2024 Nov. Arthrosc Tech. 2024. PMID: 39711889 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Colasanti CA, Mercer NP, Garcia JV, Kerkhoffs GMMJ, Kennedy JG: In-office needle arthroscopy for the treatment of anterior ankle impingement yields high patient satisfaction with high rates of return to work and sport. Arthroscopy 2022;38:1302-1311. - PubMed
-
- Zhang K, Crum RJ, Samuelsson K, Cadet E, Ayeni OR, de Sa D: In-office needle arthroscopy: A systematic review of indications and clinical utility. Arthroscopy 2019;35:2709-2721. - PubMed
-
- Gill TJ, Safran M, Mandelbaum B, Huber B, Gambardella R, Xerogeanes J: A prospective, blinded, multicenter clinical trial to compare the efficacy, accuracy, and safety of in-office diagnostic arthroscopy with magnetic resonance imaging and surgical diagnostic arthroscopy. Arthroscopy 2018;34:2429-2435. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

