Eliminating drug target interference with specific antibody or its F(ab')2 fragment in the bridging immunogenicity assay
- PMID: 38385901
- PMCID: PMC11845105
- DOI: 10.4155/bio-2023-0191
Eliminating drug target interference with specific antibody or its F(ab')2 fragment in the bridging immunogenicity assay
Abstract
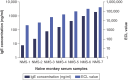
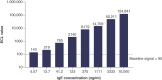
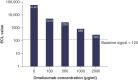
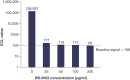
Background: DB-1003 is a humanized anti-IgE monoclonal antibody with higher affinity than omalizumab. In the affinity capture elution (ACE)-based bridging electrochemiluminescent immunoassay (ECLIA) for antibodies to DB-1003, monkey serum IgE caused false-positive results. Materials & methods: The target-specific antibody or its F(ab')2 fragment was used to mitigate drug target interference in an ACE-based bridging ECLIA for the detection of anti-DB-1003 antibodies. Results: The sensitivity of the developed assay was at least 100 ng/ml. When the anti-drug antibody concentration was 250 ng/ml, the assay tolerated at least 20.0 μg/ml of the monkey IgE. Conclusion: Incorporating the target-specific antibody or its F(ab')2 fragment can overcome the interference from monkey serum IgE in ACE-based bridging ECLIA for anti-DB-1003 antibody detection.
Keywords: IgE; anti-drug antibody; immunogenicity; mitigation; target interference.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests or relevant affiliations with any organization or entity with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. This includes employment, consultancies, stock ownership or options and expert testimony.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Preexisting Antibodies to an F(ab')2 Antibody Therapeutic and Novel Method for Immunogenicity Assessment.J Immunol Res. 2016;2016:2921758. doi: 10.1155/2016/2921758. Epub 2016 Jun 16. J Immunol Res. 2016. PMID: 27413757 Free PMC article.
-
A Monovalent Fab Affinity-Capture and Elution Bridging Immunoassay Overcomes Rheumatoid Factor Interference while Accurately Detecting Antidrug Antibodies.J Appl Lab Med. 2023 Sep 7;8(5):896-908. doi: 10.1093/jalm/jfad035. J Appl Lab Med. 2023. PMID: 37473444
-
Antibody Fragment F(ab')2 Targeting Caveolae-Associated Protein PV1 for Selective Kidney Targeting and Retention.Mol Pharm. 2020 Feb 3;17(2):507-516. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.9b00939. Epub 2019 Dec 30. Mol Pharm. 2020. PMID: 31841002
-
Natural antibodies against the immunoglobulin F(ab')2 fragment cause elimination of antigens recognized by the F(ab')2 from the circulation.Eur J Immunol. 1995 Nov;25(11):3128-33. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830251121. Eur J Immunol. 1995. PMID: 7489753
-
A recombinant humanized anti-IgE monoclonal antibody (omalizumab) in the therapy of moderate-to-severe allergic asthma.Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2007 Nov;1(3):225-31. doi: 10.2174/187221307782418900. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2007. PMID: 19075985 Review.
References
-
- Ishizaka K , Ishizaka T. Identification of IgE. J. Allergy Clin. Immun. 137(6), 1646–1650 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Johansson SGO. The discovery of IgE. J. Allergy Clin. Immun. 137(6), 1671–1673 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Schellekens H. Immunogenicity of therapeutic proteins: clinical implications and future prospects. Clin. Ther. 24(11), 1720–1740 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Ponce R , Abad L , Amaravadi Let al. . Immunogenicity of biologically-derived therapeutics: assessment and interpretation of nonclinical safety studies. Regul. Toxicol. Pharm. 54(2), 164–182 (2009). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
