MicroRNA-320a enhances LRWD1 expression through the AGO2/FXR1-dependent pathway to affect cell behaviors and the oxidative stress response in human testicular embryonic carcinoma cells
- PMID: 38385979
- PMCID: PMC10929808
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.205571
MicroRNA-320a enhances LRWD1 expression through the AGO2/FXR1-dependent pathway to affect cell behaviors and the oxidative stress response in human testicular embryonic carcinoma cells
Abstract
Background: Testicular cancer is fairly rare but can affect fertility in adult males. Leucine-rich repeats- and WD repeat domain-containing protein 1 (LRWD1) is a sperm-specific marker that mainly affects sperm motility in reproduction. Our previous study demonstrated the impact of LRWD1 on testicular cancer development; however, the underlying mechanisms remain unclear.
Methods: In this study, various plasmids associated with LRWD1 and miR-320a manipulation were used to explore the roles and regulatory effects of these molecules in NT2D1 cellular processes. A Dual-Glo luciferin-luciferase system was used to investigate LRWD1 transcriptional activity, and qRT-PCR and western blotting were used to determine gene and protein expression.
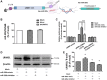
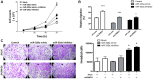
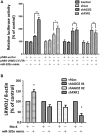
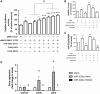
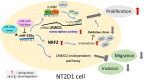
Results: The results suggested that miR-320a positively regulated LRWD1 and positively correlated with NT2D1 cell proliferation but negatively correlated with cell migration and invasion ability. In addition, the miRNA-ribonucleoprotein complex AGO2/FXR1 was shown to be essential in the mechanism by which miR-320a regulates LRWD1 mRNA expression. As miR-320a was required to regulate LRWD1 expression through the AGO2 and FXR1 complex, eEF2 and eLF4E were also found to be involved in miR-320a increasing LRWD1 expression. Furthermore, miR-320a and LRWD1 were responsive to oxidative stress, and NRF2 was affected by the presence of miR-320a in response to ROS stimulation.
Conclusions: This is the first study showing the role of miR-320a in upregulating the testicular cancer-specific regulator LRWD1 and the importance of the AGO2/FXR1 complex in miR-320a-mediated upregulation of LRWD1 during testicular cancer progression.
Keywords: AGO2; FXR1; LRWD1; miR-320a; testicular cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
LRWD1 Regulates Microtubule Nucleation and Proper Cell Cycle Progression in the Human Testicular Embryonic Carcinoma Cells.J Cell Biochem. 2018 Jan;119(1):314-326. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26180. Epub 2017 Jun 27. J Cell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 28569402
-
Nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor regulates LRWD1 expression and cellular adaptation to oxidative stress in human embryonal carcinoma cells.Biochimie. 2018 May;148:99-106. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2018.03.001. Epub 2018 Mar 12. Biochimie. 2018. PMID: 29544732
-
Downregulation of miR-320a/383-sponge-like long non-coding RNA NLC1-C (narcolepsy candidate-region 1 genes) is associated with male infertility and promotes testicular embryonal carcinoma cell proliferation.Cell Death Dis. 2015 Nov 5;6(11):e1960. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.267. Cell Death Dis. 2015. PMID: 26539909 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging role of miR-320a in lung cancer: a comprehensive review.Biomark Med. 2023 Sep;17(18):767-781. doi: 10.2217/bmm-2023-0215. Epub 2023 Dec 14. Biomark Med. 2023. PMID: 38095986 Review.
-
An in-depth review of the function of RNA-binding protein FXR1 in neurodevelopment.Cell Tissue Res. 2024 Nov;398(2):63-77. doi: 10.1007/s00441-024-03912-8. Epub 2024 Aug 19. Cell Tissue Res. 2024. PMID: 39155323 Review.
Cited by
-
Profiling the regulatory landscape of sialylation through miRNA targeting of CMP- sialic acid synthetase.J Biol Chem. 2025 Apr;301(4):108340. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.108340. Epub 2025 Feb 24. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 40010608 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in Genitourinary Malignancies: An Exciting Frontier of Cancer Diagnostics and Therapeutics.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 31;25(17):9499. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179499. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the molecular pathways of miRNAs in testicular cancer: from diagnosis to therapeutic innovations.Funct Integr Genomics. 2025 Apr 14;25(1):88. doi: 10.1007/s10142-025-01599-w. Funct Integr Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40229500 Review.
References
-
- Wang Y, Khan A, Marks AB, Smith OK, Giri S, Lin YC, Creager R, MacAlpine DM, Prasanth KV, Aladjem MI, Prasanth SG. Temporal association of ORCA/LRWD1 to late-firing origins during G1 dictates heterochromatin replication and organization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017; 45:2490–502. 10.1093/nar/gkw1211 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

