Varus osteotomy as a salvage procedure for young patients with symptomatic patellofemoral arthritis and valgus malalignment at short- to mid-term follow-up: a case series
- PMID: 38386061
- PMCID: PMC10965738
- DOI: 10.1007/s00402-024-05212-w
Varus osteotomy as a salvage procedure for young patients with symptomatic patellofemoral arthritis and valgus malalignment at short- to mid-term follow-up: a case series
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of the study was to report the clinical, functional and radiological outcome following varus osteotomy as a salvage procedure in young to middle-aged patients with patellofemoral arthritis (PFA) and associated valgus malalignment. It was hypothesized that a significant improvement in knee function and reduction in pain would be achieved. Moreover, no conversion to patellofemoral joint arthroplasty could be observed.
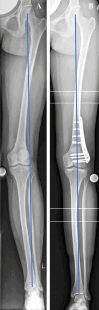
Material and methods: Patients (< 50 years of age) that underwent varus osteotomy between 08/2012 and 01/2020 for the treatment of symptomatic PFA and associated valgus malalignment were consecutively included (minimum follow-up: 24 months). Patient-reported outcome measures (PROM; International Knee Documentation Committee subjective knee form [IKDC]), Visual Analog Scale [VAS] for pain, Tegner Activity Scale [TAS], and satisfaction with the postoperative results (1-10-scale, 10 = highest satisfaction) and weight-bearing whole-leg anteroposterior radiographs were conducted pre- and postoperatively. The change in PROM and femorotibial angle (FTA) were tested for statistical significance.
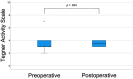
Results: In total, 12 patients (14 knees) were included (66.7% female; mean age: 33.8 ± SD 6.6 years). In ten cases, lateral opening-wedge distal femoral osteotomies (DFO) were performed, of which three cases included a concomitant femoral derotation. Three medial closing-wedge DFO and one medial closing-wedge high tibial osteotomy were performed. At follow-up (55.3 ± 29.3 months), a significant improvement in knee function (IKDC: 56.4 ± 14.4 to 69.1 ± 11.2, p = 0.015) and reduction in pain (VAS for pain: 3.5 [interquartile range 2.3-5.8] to 0.5 [0-2.0], p = 0.018) were observed. Patients were able to reach their preoperative sporting activity level (TAS: 3.0 [3.0-4.0] to 3.5 [3.0-4.0], p = 0.854) and were highly satisfied with the postoperative result (9.0 [6.5-10]). Additionally, a significant correction of valgus malalignment was observed (5.0° ± 2.9° valgus to 0.7° ± 3.2° varus, p < 0.001). Regarding complications, two re-osteosyntheses were performed due to loss of correction and delayed union. No conversion to patellofemoral arthroplasty occurred.
Conclusion: In patients with symptomatic PFA and associated valgus malalignment, varus osteotomy as a salvage procedure achieved a significant improvement in knee function and reduction in pain. No conversion to patellofemoral joint arthroplasty occurred at short- to mid-term follow-up.
Level of evidence: Retrospective case series, Level IV.
Keywords: Joint preservation; Maltracking; Patellofemoral joint; Patellofemoral osteoarthritis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Maximilian Hinz, Maximilian Weyer, Moritz Brunner, Lorenz Fritsch, Alexander Otto and Andrea Achtnich declare no conflict of interest. Sebastian Siebenlist is a consultant for Arthrex Inc., medi GmbH & Co. KG, Medartis AG, and KLS Martin Group.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lateral Opening-wedge Distal Femoral Osteotomy: Pain Relief, Functional Improvement, and Survivorship at 5 Years.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015 Jun;473(6):2009-15. doi: 10.1007/s11999-014-4106-8. Epub 2014 Dec 24. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015. PMID: 25537806 Free PMC article.
-
Derotational distal femoral osteotomy for patients with recurrent patellar instability and increased femoral antetorsion improves knee function and adequately treats both torsional and valgus malalignment.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023 Aug;31(8):3091-3097. doi: 10.1007/s00167-022-07150-9. Epub 2022 Sep 16. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023. PMID: 36109379 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Effect of Isolated Lateral Closing Wedge Distal Femoral Osteotomy Compared to Medial Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy for the Correction of Varus Malalignment: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis.Am J Sports Med. 2023 Feb;51(2):437-445. doi: 10.1177/03635465221142615. Epub 2023 Jan 11. Am J Sports Med. 2023. PMID: 36629434 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes of Distal Femoral Osteotomy for Valgus Malalignment: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Closing Wedge Versus Opening Wedge Techniques.Am J Sports Med. 2023 Mar;51(3):798-811. doi: 10.1177/03635465211051740. Epub 2022 Feb 14. Am J Sports Med. 2023. PMID: 35156408
-
Good long-term survival and patient-reported outcomes after high tibial osteotomy for medial compartment osteoarthritis.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021 Nov;29(11):3569-3584. doi: 10.1007/s00167-020-06262-4. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021. PMID: 32909057
Cited by
-
Distal femoral osteotomy for the treatment of chronic patellofemoral instability improves gait patterns.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2025 Mar 8;145(1):176. doi: 10.1007/s00402-025-05788-x. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2025. PMID: 40056196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barnavon T, Odri GA, Vendeuvre T, Labrada-Blanco O, Bordes M, Renard G, et al. Medial closing-wedge distal femoral varus osteotomy: symptoms and functional impact in cases of associated patellofemoral osteoarthritis. A two-year follow-up prospective pilot study. Knee. 2020;27:615–623. doi: 10.1016/j.knee.2020.02.001. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

