Identifying the Risk Factors of Allergic Rhinitis Based on Zhihu Comment Data Using a Topic-Enhanced Word-Embedding Model: Mixed Method Study and Cluster Analysis
- PMID: 38386404
- PMCID: PMC10921335
- DOI: 10.2196/48324
Identifying the Risk Factors of Allergic Rhinitis Based on Zhihu Comment Data Using a Topic-Enhanced Word-Embedding Model: Mixed Method Study and Cluster Analysis
Abstract
Background: Allergic rhinitis (AR) is a chronic disease, and several risk factors predispose individuals to the condition in their daily lives, including exposure to allergens and inhalation irritants. Analyzing the potential risk factors that can trigger AR can provide reference material for individuals to use to reduce its occurrence in their daily lives. Nowadays, social media is a part of daily life, with an increasing number of people using at least 1 platform regularly. Social media enables users to share experiences among large groups of people who share the same interests and experience the same afflictions. Notably, these channels promote the ability to share health information.
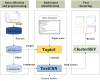
Objective: This study aims to construct an intelligent method (TopicS-ClusterREV) for identifying the risk factors of AR based on these social media comments. The main questions were as follows: How many comments contained AR risk factor information? How many categories can these risk factors be summarized into? How do these risk factors trigger AR?
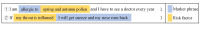
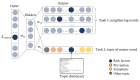
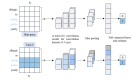
Methods: This study crawled all the data from May 2012 to May 2022 under the topic of allergic rhinitis on Zhihu, obtaining a total of 9628 posts and 33,747 comments. We improved the Skip-gram model to train topic-enhanced word vector representations (TopicS) and then vectorized annotated text items for training the risk factor classifier. Furthermore, cluster analysis enabled a closer look into the opinions expressed in the category, namely gaining insight into how risk factors trigger AR.
Results: Our classifier identified more comments containing risk factors than the other classification models, with an accuracy rate of 96.1% and a recall rate of 96.3%. In general, we clustered texts containing risk factors into 28 categories, with season, region, and mites being the most common risk factors. We gained insight into the risk factors expressed in each category; for example, seasonal changes and increased temperature differences between day and night can disrupt the body's immune system and lead to the development of allergies.
Conclusions: Our approach can handle the amount of data and extract risk factors effectively. Moreover, the summary of risk factors can serve as a reference for individuals to reduce AR in their daily lives. The experimental data also provide a potential pathway that triggers AR. This finding can guide the development of management plans and interventions for AR.
Keywords: chronic disease management; disease risk factor identification; social media platforms; text mining; topic-enhanced word embedding.
©Dongxiao Gu, Qin Wang, Yidong Chai, Xuejie Yang, Wang Zhao, Min Li, Oleg Zolotarev, Zhengfei Xu, Gongrang Zhang. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (https://www.jmir.org), 22.02.2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
-
Stigma Management Strategies of Autistic Social Media Users.Autism Adulthood. 2025 May 28;7(3):273-282. doi: 10.1089/aut.2023.0095. eCollection 2025 Jun. Autism Adulthood. 2025. PMID: 40539215
-
The Lived Experience of Autistic Adults in Employment: A Systematic Search and Synthesis.Autism Adulthood. 2024 Dec 2;6(4):495-509. doi: 10.1089/aut.2022.0114. eCollection 2024 Dec. Autism Adulthood. 2024. PMID: 40018061 Review.
-
Interventions to improve inhaler technique for people with asthma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 13;3(3):CD012286. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012286.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28288272 Free PMC article.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
Cited by
-
Identifying Kidney Stone Risk Factors Through Patient Experiences With a Large Language Model: Text Analysis and Empirical Study.J Med Internet Res. 2025 May 22;27:e66365. doi: 10.2196/66365. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 40403294 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of immunoglobulin E sensitization to various inhaled allergens among the residents of the Northern United Arab Emirates: Automated evaluation of a membrane-based test system.Saudi Med J. 2025 Mar;46(3):282-291. doi: 10.15537/smj.2025.46.3.20240929. Saudi Med J. 2025. PMID: 40096981 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Linguistic Signals on Cognitive Change in Support Seekers in Online Mental Health Communities: Text Analysis and Empirical Study.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Jan 14;27:e60292. doi: 10.2196/60292. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 39808783 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Krishna MT, Mahesh PA, Vedanthan PK, Mehta V, Moitra S, Christopher DJ. The burden of allergic diseases in the Indian subcontinent: barriers and challenges. Lancet Glob Health. 2020 Apr;8(4):e478–9. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30061-9. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2214-109X(20)30061-9 S2214-109X(20)30061-9 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang XD, Zheng M, Lou HF, Wang CS, Zhang Y, Bo MY, Ge SQ, Zhang N, Zhang L, Bachert C. An increased prevalence of self-reported allergic rhinitis in major Chinese cities from 2005 to 2011. Allergy. 2016 Aug 13;71(8):1170–80. doi: 10.1111/all.12874. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/26948849 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Price D, Smith P, Hellings P, Papadopoulos N, Fokkens W, Muraro A, Murray R, Chisholm A, Demoly P, Scadding G, Mullol J, Lieberman P, Bachert C, Mösges R, Ryan D, Bousquet J. Current controversies and challenges in allergic rhinitis management. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2015 Aug 29;11(11):1205–17. doi: 10.1586/1744666x.2015.1081814. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

