European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging survey on the evaluation of mitral regurgitation
- PMID: 38387435
- PMCID: PMC11057920
- DOI: 10.1093/ehjci/jeae053
European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging survey on the evaluation of mitral regurgitation
Erratum in
-
Correction to: European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging survey on the evaluation of mitral regurgitation.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2024 Jul 31;25(8):e202. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jeae151. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38905439 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Aims: To evaluate the diagnosis and imaging of patients with mitral regurgitation (MR) and the management in routine clinical practice across Europe, the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging Scientific Initiatives Committee performed a survey across European centres. In particular, the routine use of echocardiography, advanced imaging modalities, heart valve clinics, and heart valve teams was explored.
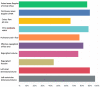
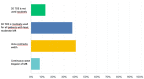
Methods and results: A total of 61 responders, mainly from tertiary centres or university hospitals, from 26 different countries responded to the survey, which consisted of 22 questions. For most questions related to echocardiography and advanced imaging, the answers were relatively homogeneous and demonstrated good adherence to current recommendations. In particular, the centres used a multi-parametric echocardiographic approach and selected the effective regurgitant orifice and vena contracta width as their preferred assessments. 2D measurements are still the most widely used parameters to assess left ventricular structure; however, the majority use 3D trans-oesophageal echocardiography (TOE) to evaluate valve morphology in severe MR. The majority of centres reported the onsite availability and clinical use of ergometric stress echocardiography, cardiac computed tomography (CCT), and cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging. Heart valve clinics and heart valve teams were also widely prevalent.
Conclusion: Consistent with current guidelines, echocardiography (transthoracic echocardiography and TOE) remains the first-line and central imaging modality for the assessment of MR although the complementary use of 3D TOE, CCT, and CMR appears to be growing. Heart valve clinics and heart valve teams are now widely prevalent.
Keywords: CMR; EACVI; cardiac CT; echocardiography; mitral regurgitation.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None declared.
Figures


References
-
- Iung B, Delgado V, Rosenhek R, Price S, Prendergast B, Wendler O et al. Contemporary presentation and management of valvular heart disease: the EURObservational research programme valvular heart disease II survey. Circulation 2019;140:1156–69. - PubMed
-
- Vahanian A, Beyersdorf F, Praz F, Milojevic M, Baldus S, Bauersachs J et al. 2021 ESC/EACTS guidelines for the management of valvular heart disease. Eur Heart J 2022;43:561–632. - PubMed
-
- Haugaa KH, Marsan NA, Cameli M, 'Andrea D, Dweck A, Carvalho MR et al. Criteria for surveys: from the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging Scientific Initiatives Committee. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 2019;20:963–6. - PubMed
-
- Cameli M, Marsan NA, D'Andrea A, Dweck MR, Fontes-Carvalho R, Manka R et al. EACVI survey on multimodality training in ESC countries. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 2019;20:1332–6. - PubMed

