Production and characterization of novel marine black yeast's exopolysaccharide with potential antiradical and anticancer prospects
- PMID: 38388439
- PMCID: PMC10882794
- DOI: 10.1186/s12934-024-02332-1
Production and characterization of novel marine black yeast's exopolysaccharide with potential antiradical and anticancer prospects
Abstract
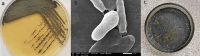
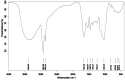
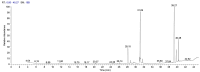
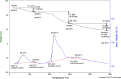
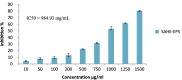
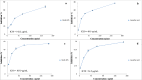
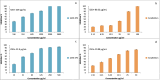
The marine black yeasts are characterized by the production of many novel protective substances. These compounds increase their physiological adaptation to multi-extreme environmental stress. Hence, the exopolysaccharide (EPS) producing marine black yeast SAHE was isolated in this study. It was molecularly identified as Hortaea werneckii (identity 98.5%) through ITS1 and ITS4 gene sequencing analysis. The physicochemical properties of the novel SAHE-EPS were investigated through FTIR, GC-MS, TGA, ESM, and EDX analysis, revealing its heteropolysaccharide nature. SAHE-EPS was found to be thermostable and mainly consists of sucrose, maltose, cellobiose, lactose, and galactose. Furthermore, it exhibited an amorphous texture and irregular porous surface structure. SAHE-EPS showed significant antiradical activity, as demonstrated by the DPPH radical scavenging assay, and the IC50 was recorded to be 984.9 μg/mL. In addition, SAHE-EPS exhibited outstanding anticancer activity toward the A549 human lung cancer cell line (IC50 = 22.9 μg/mL). Conversely, it demonstrates minimal cytotoxicity toward the WI-38 normal lung cell line (IC50 = 203 μg/mL), which implies its safety. This study represents the initial attempt to isolate and characterize the chemical properties of an EPS produced by the marine black yeast H. werneckii as a promising antiradical and anticancer agent.
Keywords: Anticancer; Black yeast; Chemical characterization; Exopolysaccharide; Hortaea Werneckii.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Optimization of melanin pigment production from the halotolerant black yeast Hortaea werneckii AS1 isolated from solar salter in Alexandria.BMC Microbiol. 2022 Apr 8;22(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s12866-022-02505-1. BMC Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35395716 Free PMC article.
-
Suggested Sustainable Medical and Environmental Uses of Melanin Pigment From Halotolerant Black Yeast Hortaea werneckii AS1.Front Microbiol. 2022 Apr 13;13:871394. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.871394. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35495654 Free PMC article.
-
Salt stress affects sterol biosynthesis in the halophilic black yeast Hortaea werneckii.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1999 Nov 15;180(2):325-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1999.tb08813.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1999. PMID: 10556729
-
Production and Characterization of Exopolysaccharide From Newly Isolated Marine Probiotic Lactiplantibacillus plantarum EI6 With in vitro Wound Healing Activity.Front Microbiol. 2022 May 13;13:903363. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.903363. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35668753 Free PMC article.
-
Growth and division mode plasticity is dependent on cell density in marine-derived black yeasts.Genes Cells. 2022 Feb;27(2):124-137. doi: 10.1111/gtc.12916. Epub 2021 Dec 30. Genes Cells. 2022. PMID: 34932251
References
-
- Garza-Rodríguez ZB, Hernández-Pérez J, Santacruz A, Jacobo-Velázquez DA, Benavides JJCRiB. Prospective on the application of abiotic stresses to enhance the industrial production of exopolysaccharides from microalgae. 2022.
-
- Wu Z, Yang Z, Gan D, Fan J, Dai Z, Wang X, Hu B, Ye H, Abid M, Zeng XJB. Bioenergy: influences of carbon sources on the biomass, production and compositions of exopolysaccharides from Paecilomyces Hepiali HN1. 2014;67:260–9.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

