Anthropogenic aerosols mask increases in US rainfall by greenhouse gases
- PMID: 38388495
- PMCID: PMC10884021
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-45504-8
Anthropogenic aerosols mask increases in US rainfall by greenhouse gases
Abstract
A comprehensive understanding of human-induced changes to rainfall is essential for water resource management and infrastructure design. However, at regional scales, existing detection and attribution studies are rarely able to conclusively identify human influence on precipitation. Here we show that anthropogenic aerosol and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions are the primary drivers of precipitation change over the United States. GHG emissions increase mean and extreme precipitation from rain gauge measurements across all seasons, while the decadal-scale effect of global aerosol emissions decreases precipitation. Local aerosol emissions further offset GHG increases in the winter and spring but enhance rainfall during the summer and fall. Our results show that the conflicting literature on historical precipitation trends can be explained by offsetting aerosol and greenhouse gas signals. At the scale of the United States, individual climate models reproduce observed changes but cannot confidently determine whether a given anthropogenic agent has increased or decreased rainfall.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
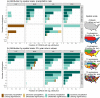

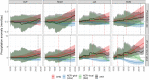

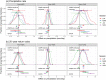
References
-
- Trenberth K. Changes in precipitation with climate change. Clim. Res. 2011;47:123–138. doi: 10.3354/cr00953. - DOI
-
- Siirila-Woodburn ER, et al. A low-to-no snow future and its impacts on water resources in the western United States. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021;2:800–819. doi: 10.1038/s43017-021-00219-y. - DOI
-
- Huss M, Hock R. Global-scale hydrological response to future glacier mass loss. Nat. Clim. Change. 2018;8:135–140. doi: 10.1038/s41558-017-0049-x. - DOI
-
- Taylor RG, et al. Ground water and climate change. Nat. Clim. Change. 2013;3:322–329. doi: 10.1038/nclimate1744. - DOI
-
- Pörtner, H. O. et al. Summary for policymakers. In Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, 3–33 (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, 2022).

