MIRD Pamphlet No. 29: MIRDy90-A 90Y Research Microsphere Dosimetry Tool
- PMID: 38388514
- PMCID: PMC11064830
- DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.123.266743
MIRD Pamphlet No. 29: MIRDy90-A 90Y Research Microsphere Dosimetry Tool
Abstract
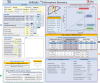
90Y-microsphere radioembolization has become a well-established treatment option for liver malignancies and is one of the first U.S. Food and Drug Administration-approved unsealed radionuclide brachytherapy devices to incorporate dosimetry-based treatment planning. Several different mathematical models are used to calculate the patient-specific prescribed activity of 90Y, namely, body surface area (SIR-Spheres only), MIRD single compartment, and MIRD dual compartment (partition). Under the auspices of the MIRDsoft initiative to develop community dosimetry software and tools, the body surface area, MIRD single-compartment, MIRD dual-compartment, and MIRD multicompartment models have been integrated into a MIRDy90 software worksheet. The worksheet was built in MS Excel to estimate and compare prescribed activities calculated via these respective models. The MIRDy90 software was validated against available tools for calculating 90Y prescribed activity. The results of MIRDy90 calculations were compared with those obtained from vendor and community-developed tools, and the calculations agreed well. The MIRDy90 worksheet was developed to provide a vetted tool to better evaluate patient-specific prescribed activities calculated via different models, as well as model influences with respect to varying input parameters. MIRDy90 allows users to interact and visualize the results of various parameter combinations. Variables, equations, and calculations are described in the MIRDy90 documentation and articulated in the MIRDy90 worksheet. The worksheet is distributed as a free tool to build expertise within the medical physics community and create a vetted standard for model and variable management.
Keywords: 90Y-microspheres; MIRD dual-compartment dosimetry; partition model dosimetry; radioembolization; selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT).
© 2024 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MIRD Pamphlet No. 30: MIRDfit-A Tool for Fitting of Biodistribution Time-Activity Data for Internal Dosimetry.J Nucl Med. 2024 Nov 1;65(11):1808-1814. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.124.268011. J Nucl Med. 2024. PMID: 39327016 Free PMC article.
-
MIRD Pamphlet No. 28, Part 1: MIRDcalc-A Software Tool for Medical Internal Radiation Dosimetry.J Nucl Med. 2023 Jul;64(7):1117-1124. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.122.264225. Epub 2023 Jun 2. J Nucl Med. 2023. PMID: 37268428 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of end-to-end 3D absorbed dose distribution in 90Y-SIRT and SBRT combination therapy using MAGIC-f polymer gel dosimeter.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2025 Aug 8. doi: 10.1007/s00259-025-07461-2. Online ahead of print. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40779067
References
-
- Elsayed M, Cheng B, Xing M, et al. . Comparison of Tc-99m MAA planar versus SPECT/CT imaging for lung shunt fraction evaluation prior to Y-90 radioembolization: are we overestimating lung shunt fraction? Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2021;44:254–260. - PubMed
-
- Struycken L, Patel M, Kuo P, Hennemeyer C, Woodhead G, McGregor H. Clinical and dosimetric implications of calculating lung shunt fraction for hepatic 90Y radioembolization using SPECT/CT versus planar scintigraphy. AJR. 2022;218:728–737. - PubMed
-
- Ahmadzadehfar H, Sabet A, Biermann K, et al. . The significance of 99mTc-MAA SPECT/CT liver perfusion imaging in treatment planning for 90Y-microsphere selective internal radiation treatment. J Nucl Med. 2010;51:1206–1212. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
