Emergence of a clinical Salmonella enterica serovar 1,4,[5], 12: i:-isolate, ST3606, in China with susceptibility decrease to ceftazidime-avibactam carrying a novel blaCTX-M-261 variant and a blaNDM-5
- PMID: 38388738
- PMCID: PMC11108873
- DOI: 10.1007/s10096-024-04765-3
Emergence of a clinical Salmonella enterica serovar 1,4,[5], 12: i:-isolate, ST3606, in China with susceptibility decrease to ceftazidime-avibactam carrying a novel blaCTX-M-261 variant and a blaNDM-5
Abstract
Purpose: The detection rate of Salmonella enterica serovar 1,4,[5], 12: i: - (S. 1,4,[5], 12: i: -) has increased as the most common serotype globally. A S. 1,4,[5], 12: i: - strain named ST3606 (sequence type 34), isolated from a fecal specimen of a child with acute diarrhea hospitalized in a tertiary hospital in China, was firstly reported to be resistant to carbapenem and ceftazidime-avibactam. The aim of this study was to characterize the whole-genome sequence of S. 1,4,[5], 12: i: - isolate, ST3606, and explore its antibiotic resistance genes and their genetic environments.
Methods: The genomic DNA of S. 1,4,[5], 12: i: - ST3606 was extracted and performed with single-molecule real-time sequencing. Resistance genes, plasmid replicon type, mobile elements, and multilocus sequence types (STs) of ST3606 were identified by ResFinder 3.2, PlasmidFinder, OriTfinder database, ISfinder database, and MLST 2.0, respectively. The conjugation experiment was utilized to evaluate the conjugation frequency of pST3606-2. Protein expression and enzyme kinetics experiments of CTX-M were performed to analyze hydrolytic activity of a novel CTX-M-261 enzyme toward several antibiotics.
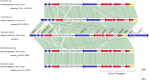
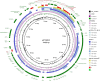
Results: Single-molecule real-time sequencing revealed the coexistence of a 109-kb IncI1-Iα plasmid pST3606-1 and a 70.5-kb IncFII plasmid pST3606-2. The isolate carried resistance genes, including blaNDM-5, sul1, qacE, aadA2, and dfrA12 in pST3606-1, blaTEM-1B, aac(3)-lld, and blaCTX-M-261, a novel blaCTX-M-1 family member, in pST3606-2, and aac(6')-Iaa in chromosome. The blaCTX-M-261 was derived from blaCTX-M-55 by a single-nucleotide mutation 751G>A leading to amino acid substitution of Val for Met at position 251 (Val251Met), which conferred CTX-M increasing resistance to ceftazidime verified by antibiotics susceptibility testing of transconjugants carrying pST3606-2 and steady-state kinetic parameters of CTX-M-261. pST3606-1 is an IncI1-α incompatibility type that shares homology with plasmids of pC-F-164_A-OXA140, pE-T654-NDM-5, p_dm760b_NDM-5, and p_dmcr749c_NDM-5. The conjugation experiment demonstrated that pST3606-2 was successfully transferred to the Escherichia coli recipient C600 with four modules of OriTfinder.
Conclusion: Plasmid-mediated horizontal transfer plays an important role in blaNDM-5 and blaCTX-M-261 dissemination, which increases the threat to public health due to the resistance to most β-lactam antibiotics. This is the first report of blaCTX-M-261 and blaNDM-5 in S. 1,4,[5], 12: i: -. The work provides insights into the enzymatic function and demonstrates the ongoing evolution of CTX-M enzymes and confirms urgency to control resistance of S. 1,4,[5], 12: i: -.
Keywords: Bla CTX-M-261; Bla NDM-5; Salmonella enterica serovar 1,4,[5]; 12: i: -; Ceftazidime-avibactam; IncI1-I(α).
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Stool carriage of CTX-M/CMY-producing Salmonella enterica in a Chinese tertiary hospital in Shenzhen, China.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Mar 13;15:1544757. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1544757. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40182768 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of Citrobacter freundii clinical isolates in a Chinese hospital during 2020-2022 revealed genomic characterization of an extremely drug-resistant C. freundii ST257 clinical strain GMU8049 co-carrying blaNDM-1 and a novel blaCMY variant.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Nov 5;12(11):e0425423. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.04254-23. Epub 2024 Oct 10. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 39387591 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic and molecular characterization of a ceftazidime-avibactam resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae strain isolated from a Chinese tertiary hospital.BMC Microbiol. 2025 Apr 8;25(1):199. doi: 10.1186/s12866-025-03929-1. BMC Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40200176 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic characterization of an extensively-drug resistance Salmonella enterica serotype Indiana strain harboring blaNDM-1 gene isolated from a chicken carcass in China.Microbiol Res. 2017 Nov;204:48-54. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2017.07.006. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Microbiol Res. 2017. PMID: 28870291
-
Co-carrying of KPC-2, NDM-5, CTX-M-3 and CTX-M-65 in three plasmids with serotype O89: H10 Escherichia coli strain belonging to the ST2 clone in China.Microb Pathog. 2019 Mar;128:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.12.033. Epub 2018 Dec 18. Microb Pathog. 2019. PMID: 30576714
Cited by
-
Genomic analyses reveal presence of extensively drug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovars isolated from clinical samples in Guizhou province, China, 2019-2023.Front Microbiol. 2025 Mar 27;16:1532036. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1532036. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40226105 Free PMC article.
-
Plasmid-driven clonal expansion of multidrug-resistant monophasic Salmonella Typhimurium in a Global Food Trade Hub.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2025 Dec;14(1):2542251. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2025.2542251. Epub 2025 Aug 10. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2025. PMID: 40785095 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tennant SM, Diallo S, Levy H, Livio S, Sow SO, Tapia M, Fields PI, Mikoleit M, Tamboura B, Kotloff KL, Nataro JP, Galen JE, Levine MM. Identification by PCR of non-typhoidal Salmonella enterica serovars associated with invasive infections among febrile patients in Mali. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2010;4(3):e621. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000621. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2022A1515110558/GuangDong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation
- 2023XSYC-03/Xiangshan Talent Project of Zhuhai People's Hospital
- 2023LCTS-01/Clinical Research Promotion Project of Zhuhai People's Hospital
- 2019PY-29/Cultivation Project of Zhuhai People's Hospital
- 202201020039/Guangzhou science and technology plan project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

