Analysis of the cytotoxicity and bioactivity of CeraSeal, BioRoot™ and AH Plus® sealers in pre-osteoblast lineage cells
- PMID: 38389110
- PMCID: PMC10882839
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-024-04021-2
Analysis of the cytotoxicity and bioactivity of CeraSeal, BioRoot™ and AH Plus® sealers in pre-osteoblast lineage cells
Abstract
Background: The objective of the present study was to evaluate in vitro the cytotoxicity and bioactivity of various endodontic sealers (CeraSeal, BioRoot™ and AH Plus®) in pre-osteoblast mouse cells (MC3T3 cells).
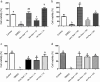
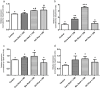
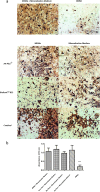
Methods: MC3T3 cells (ATCC CRL-2594) were plated in 1 × 104 cells/well in 96-well plates in contact with endodontic sealers at concentrations of 1:10 and 1:100. Cell viability was evaluated by MTT assay after 24 and 48 h. In addition, sealer bioactivity was measured by RT-PCR for mediator of inflammation (Tnf, Ptgs2) and mineralization (Runx2, Msx1, Ssp1 and Dmp1) after 24 h and by Alizarin Red S Assay of mineralization after 28 days. Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey's post-test at a significance level of 5%.
Results: BioRoot™ presented 24-hour cytotoxicity (p < 0.05) at 1:10 concentration. In the period of 48 h, no endodontic cement was cytotoxic to the cells compared to the control (p > 0.05). TNF-α gene expression was induced by AH Plus® (p < 0.05), while Ptgs2 was induced by the CeraSeal and BioRoot™ (p < 0.05). The expression of Runx2 was stimulated by BioRoot™ and AH Plus® (p < 0.05). In contrast, the expression of Dmp-1 Dmp1 was higher for the CeraSeal and BioRoot™ (p < 0.05). Nonetheless, the sealers did not impact the formation of mineralization nodules (p > 0.05).
Conclusion: CeraSeal, BioRoot™ and AH Plus® sealers were not cytotoxic to MC3T3 cells within 48 h, but differentially induced the expression of genes related to inflammation and mineralization without impacting biomineralization by the cells.
Keywords: Biomineralization; Cytotoxicity; Inflammation; Osteoblasts; Root canal filling materials.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
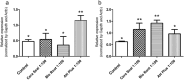
Similar articles
-
Comparative analysis of the inflammatory response of human gingival fibroblasts to NeoSEALER Flo and CeraSeal bioceramic sealers: an in vitro study.BMC Oral Health. 2025 Mar 17;25(1):395. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-05692-1. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40098184 Free PMC article.
-
Push-Out Bond Strength, Characterization, and Ion Release of Premixed and Powder-Liquid Bioceramic Sealers with or without Gutta-Percha.Scanning. 2021 May 6;2021:6617930. doi: 10.1155/2021/6617930. eCollection 2021. Scanning. 2021. PMID: 34040690 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive in vitro comparison of the biological and physicochemical properties of bioactive root canal sealers.Clin Oral Investig. 2022 Oct;26(10):6209-6222. doi: 10.1007/s00784-022-04570-2. Epub 2022 Jun 3. Clin Oral Investig. 2022. PMID: 35660956 Free PMC article.
-
Cytotoxicity comparison of Bio C Sealer against multiple root canal sealers.J Clin Exp Dent. 2023 Feb 1;15(2):e110-e117. doi: 10.4317/jced.59868. eCollection 2023 Feb. J Clin Exp Dent. 2023. PMID: 36911158 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive review of current endodontic sealers.Dent Mater J. 2020 Sep 29;39(5):703-720. doi: 10.4012/dmj.2019-288. Epub 2020 Mar 24. Dent Mater J. 2020. PMID: 32213767 Review.
Cited by
-
Randomised Clinical Trial: Effect of AH Plus and Neosealer Flo on Postoperative Pain and Healing of Periapical Lesions.Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 Apr 2;12(4):376. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12040376. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40281736 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of the inflammatory response of human gingival fibroblasts to NeoSEALER Flo and CeraSeal bioceramic sealers: an in vitro study.BMC Oral Health. 2025 Mar 17;25(1):395. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-05692-1. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40098184 Free PMC article.
-
Biocompatibility, bioactivity and immunomodulatory properties of three calcium silicate-based sealers: an in vitro study on hPDLSCs.Clin Oral Investig. 2024 Jul 6;28(8):416. doi: 10.1007/s00784-024-05812-1. Clin Oral Investig. 2024. PMID: 38969964 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goldberg M, Hirata A. The dental pulp: composition, properties and functions. JSM Dent. 2017;5(1):1079.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

