Remaining life expectancy of Korean hemodialysis patients: how much longer can they live?
- PMID: 38389145
- PMCID: PMC11467359
- DOI: 10.23876/j.krcp.23.241
Remaining life expectancy of Korean hemodialysis patients: how much longer can they live?
Abstract
Background: Hemodialysis (HD) patients have a higher mortality rate compared to the general population. However, no study has investigated life expectancy in Korean HD patients so far. Therefore, this study aimed to calculate the remaining life expectancy among Korean maintenance HD patients and compare it to those of the general population as well as HD patients from other countries.
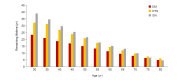
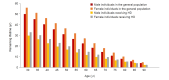
Methods: Baseline data were retrieved from HD quality assessment data from 2015. Among the patients over 30 years old who were alive at the beginning of 2016 (20,304 males and 14,264 females), a total of 22,078 (12,621 males and 9,457 females) were still alive at the end of 2021 while 12,490 (7,683 males and 4,807 females) were deceased during 6 years of follow-up. We used the life table method to calculate the expected remaining years of life in 2-year increments.
Results: The remaining life expectancies for 60-year-old patients were 11.64 years for males and 14.64 years for females. The average remaining life expectancies of the HD population were only about half of the general population. Diabetic patients demonstrated shorter life expectancy compared to patients with hypertension or glomerulonephritis. The remaining life expectancy of Korean HD patients was similar to that of Japanese and was almost double that of HD patients in Western countries such as Europe and the United States.
Conclusion: The HD population shows a shorter life expectancy compared to the general population. Longitudinal analysis should be warranted to analyze the effect of advanced dialysis technology on improved survival rates among the HD population.
Keywords: Health care outcome assessment; Life expectancy; Renal dialysis; Survival.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[REIN Report 2011--summary].Nephrol Ther. 2013 Sep;9 Suppl 1:S3-6. doi: 10.1016/S1769-7255(13)70036-1. Nephrol Ther. 2013. PMID: 24119584 French.
-
[The Veneto Region's Registry of Dialysis and Transplantation: 2006-2007 report].G Ital Nefrol. 2009 Nov-Dec;26 Suppl 48:S5-56. G Ital Nefrol. 2009. PMID: 19927265 Italian.
-
A study on patterns in the average life expectancies and mortality rates of 56 nationalities in China in 1990.Chin J Popul Sci. 1994;6(3):263-79. Chin J Popul Sci. 1994. PMID: 12319168
-
Survival Outcomes of Hemoperfusion and Hemodialysis versus Hemodialysis in Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Blood Purif. 2022;51(3):213-225. doi: 10.1159/000514187. Epub 2021 May 10. Blood Purif. 2022. PMID: 33971651 Free PMC article.
-
Dialysis Modality and Mortality in the Elderly: A Meta-Analysis.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015 Jun 5;10(6):983-93. doi: 10.2215/CJN.05160514. Epub 2015 May 4. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 25941194 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The current state of life expectancy of hemodialysis patients in Korea.Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2024 Sep;43(5):562-564. doi: 10.23876/j.krcp.24.099. Epub 2024 May 29. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2024. PMID: 38934041 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

